Page 183 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 183
Design procedures 169
intersects the breakthrough curves at the desired breakthrough concentra-
tion is then drawn to determine the breakthrough volume for each column.
The empty bed contact time (EBCT) is defined as follows:
bed volume
EBCT = (6.54)
flowrate
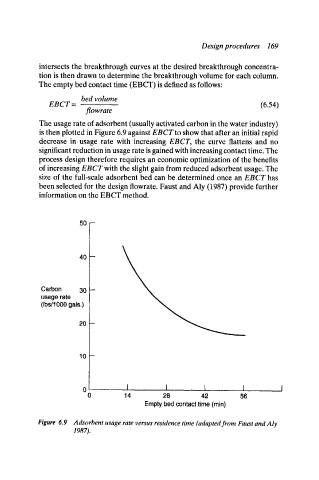
The usage rate of adsorbent (usually activated carbon in the water industry)
is then plotted in Figure 6.9 against EBCT to show that after an initial rapid
decrease in usage rate with increasing EBCT, the curve flattens and no
significant reduction in usage rate is gained with increasing contact time. The
process design therefore requires an economic optimization of the benefits
of increasing EBCT with the slight gain from reduced adsorbent usage. The
size of the full-scale adsorbent bed can be determined once an EBCT has
been selected for the design flowrate. Faust and Aly (1987) provide further
information on the EBCT method.
50--
40
Carbon 30
usage rate
(Ibs/lO00 gals.)
20
10
...... I I I
O ,, , I
0 14
28 42 56
Empty bed contact time (min)
Figure 6.9 Adsorbent usage rate versus residence time (adapted from Faust and Aly
1987).