Page 216 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 216
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH003.qxd 7/13/2006 1:46 PM Page 212
212 3. Heterogeneous Processes and Reactor Analysis
In this equation, CGS units should be used.
So, the actual bubble diameter at height z aboe the bed bottom is v
d d 0.3 z
bub,ma x bub exp
d d D (3.505)
bub,ma x bub,o
This equation has been deduced from studies conducted with bed diameters of 7.6–130
cm, minimum fluidization velocities of 0.5–20 cm/s, solid particle sizes of 0.006–0.045
cm, and u s – u fm 48 cm/s. To calculate an aalue of the bubble v an a elocity , v erage v er- v
age bubble diameter should be used. This diameter can be taken to be equal to the b ubble
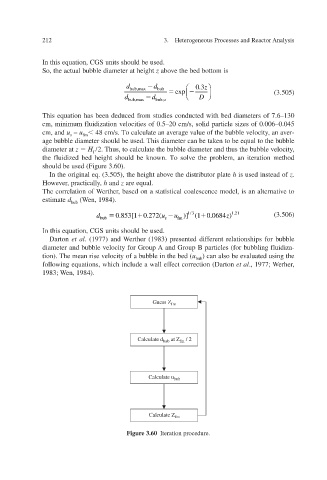
diameter at z H f /2. to calculate the bubble diameter and thus the b Thus, , elocity ubble v
the fluidized bed height should be known. To solve the problem, an iteration method
should be used (Figure 3.60).
In the original eq. (3.505), the height aboe the distributor plate v h is used instead of z .
However, practically , h and z are equal.
erther
,
The correlation of W based on a statistical coalescence model, is an alternatie to v
estimate d bub (Wen, 1984).
d 0.853[1 0.272( )] (1 u 0.0684 ) u 1 3 z 1.21 (3.506)
bub s fm
In this equation, CGS units should be used.
Darton et al . (1977) and Werther (1983) presented different relationships for b ubble
diameter and bubble velocity for Group A and Group B particles (for bubbling fluidiza-
tion). The mean rise velocity of a bubble in the bed ( u bub ) can also be ealuated using the v
following equations, which include a wall effect correction (Darton et al ., 1977; W , erher
1983; Wen, 1984).
Guess Z fm
Calculate d bub at Z fm / 2
Calculate u bub
Calculate Z fm
Figure 3.60 Iteration procedure.