Page 454 - Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of Structures
P. 454
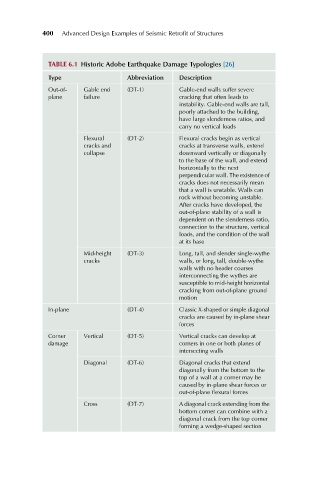
400 Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of Structures
TABLE 6.1 Historic Adobe Earthquake Damage Typologies [26]
Type Abbreviation Description
Out-of- Gable end (DT-1) Gable-end walls suffer severe
plane failure cracking that often leads to
instability. Gable-end walls are tall,
poorly attached to the building,
have large slenderness ratios, and
carry no vertical loads
Flexural (DT-2) Flexural cracks begin as vertical
cracks and cracks at transverse walls, extend
collapse downward vertically or diagonally
to the base of the wall, and extend
horizontally to the next
perpendicular wall. The existence of
cracks does not necessarily mean
that a wall is unstable. Walls can
rock without becoming unstable.
After cracks have developed, the
out-of-plane stability of a wall is
dependent on the slenderness ratio,
connection to the structure, vertical
loads, and the condition of the wall
at its base
Mid-height (DT-3) Long, tall, and slender single-wythe
cracks walls, or long, tall, double-wythe
walls with no header courses
interconnecting the wythes are
susceptible to mid-height horizontal
cracking from out-of-plane ground
motion
In-plane (DT-4) Classic X-shaped or simple diagonal
cracks are caused by in-plane shear
forces
Corner Vertical (DT-5) Vertical cracks can develop at
damage corners in one or both planes of
intersecting walls
Diagonal (DT-6) Diagonal cracks that extend
diagonally from the bottom to the
top of a wall at a corner may be
caused by in-plane shear forces or
out-of-plane flexural forces
Cross (DT-7) A diagonal crack extending from the
bottom corner can combine with a
diagonal crack from the top corner
forming a wedge-shaped section