Page 791 - Advanced_Engineering_Mathematics o'neil
P. 791
23.2 Construction of Conformal Mappings 771
y
i
x
−i
v
i
1
u
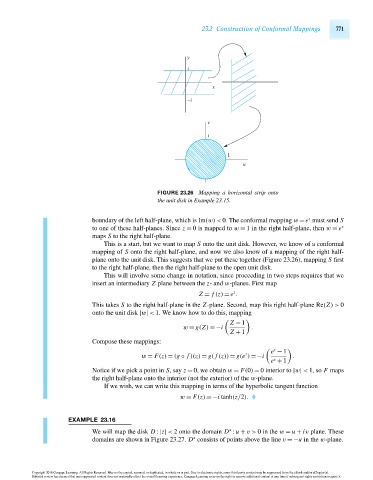
FIGURE 23.26 Mapping a horizontal strip onto
the unit disk in Example 23.15.
z
boundary of the left half-plane, which is Im(w)<0. The conformal mapping w =e must send S
to one of these half-planes. Since z = 0 is mapped to w = 1 in the right half-plane, then w = e z
maps S to the right half-plane.
This is a start, but we want to map S onto the unit disk. However, we know of a conformal
mapping of S onto the right half-plane, and now we also know of a mapping of the right half-
plane onto the unit disk. This suggests that we put these together (Figure 23.26), mapping S first
to the right half-plane, then the right half-plane to the open unit disk.
This will involve some change in notation, since proceeding in two steps requires that we
insert an intermediary Z plane between the z- and w-planes. First map
z
Z = f (z) = e .
This takes S to the right half-plane in the Z-plane. Second, map this right half-plane Re(Z)> 0
onto the unit disk |w| < 1. We know how to do this, mapping
Z − 1
w = g(Z) =−i .
Z + 1
Compose these mappings:
z
e − 1
z
w = F(z) = (g ◦ f )(z) = g( f (z)) = g(e ) =−i .
z
e + 1
Notice if we pick a point in S,say z = 0, we obtain w = F(0) = 0 interior to |w| < 1, so F maps
the right half-plane onto the interior (not the exterior) of the w-plane.
If we wish, we can write this mapping in terms of the hyperbolic tangent function
w = F(z) =−i tanh(z/2).
EXAMPLE 23.16
∗
We will map the disk D :|z| < 2 onto the domain D : u + v> 0inthe w = u + iv plane. These
domains are shown in Figure 23.27. D consists of points above the line v =−u in the w-plane.
∗
Copyright 2010 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.
October 14, 2010 15:39 THM/NEIL Page-771 27410_23_ch23_p751-788