Page 239 - Advanced Thermodynamics for Engineers, Second Edition
P. 239
10.6 EXAMPLES 227
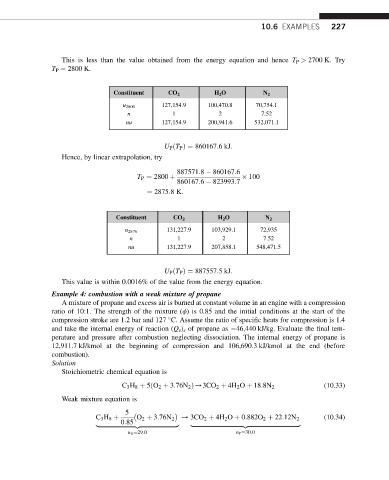
This is less than the value obtained from the energy equation and hence T P > 2700 K. Try
T P ¼ 2800 K.
Constituent CO 2 H 2 O N 2
127,154.9 100,470.8 70,754.1
u 2800
n 1 2 7.52
nu 127,154.9 200,941.6 532,071.1
U P ðT P Þ¼ 860167:6kJ:
Hence, by linear extrapolation, try
887571:8 860167:6
100
860167:6 823993:7
T P ¼ 2800 þ
¼ 2875:8K:
Constituent CO 2 H 2 O N 2
u 2876 131,227.9 103,929.1 72,935
n 1 2 7.52
nu 131,227.9 207,858.1 548,471.5
U P ðT P Þ¼ 887557:5kJ:
This value is within 0.0016% of the value from the energy equation.
Example 4: combustion with a weak mixture of propane
A mixture of propane and excess air is burned at constant volume in an engine with a compression
ratio of 10:1. The strength of the mixture (f) is 0.85 and the initial conditions at the start of the
compression stroke are 1.2 bar and 127 C. Assume the ratio of specific heats for compression is 1.4
and take the internal energy of reaction (Q v ) s of propane as 46,440 kJ/kg. Evaluate the final tem-
perature and pressure after combustion neglecting dissociation. The internal energy of propane is
12,911.7 kJ/kmol at the beginning of compression and 106,690.3 kJ/kmol at the end (before
combustion).
Solution
Stoichiometric chemical equation is
C 3 H 8 þ 5ðO 2 þ 3:76N 2 Þ/3CO 2 þ 4H 2 O þ 18:8N 2 (10.33)
Weak mixture equation is
5
O 2 þ 3:76N 2 / 3CO 2 þ 4H 2 O þ 0:882O 2 þ 22:12N 2 (10.34)
C 3 H 8 þ
0:85
|fflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflffl{zfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflffl} |fflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflffl{zfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflfflffl}
n R ¼29:0 n P ¼30:0