Page 109 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 109
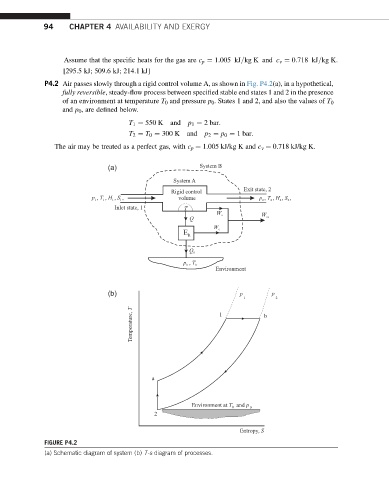
94 CHAPTER 4 AVAILABILITY AND EXERGY
Assume that the specific heats for the gas are c p ¼ 1:005 kJ=kg K and c v ¼ 0:718 kJ=kg K:
[295.5 kJ; 509.6 kJ; 214.1 kJ]
P4.2 Air passes slowly through a rigid control volume A, as shown in Fig. P4.2(a), in a hypothetical,
fully reversible, steady-flow process between specified stable end states 1 and 2 in the presence
of an environment at temperature T 0 and pressure p 0 . States 1 and 2, and also the values of T 0
and p 0 , are defined below.
T 1 ¼ 550 K and p 1 ¼ 2 bar:
T 2 ¼ T 0 ¼ 300 K and p 2 ¼ p 0 ¼ 1 bar:
The air may be treated as a perfect gas, with c p ¼ 1.005 kJ/kg K and c v ¼ 0.718 kJ/kg K.
(a) System B
System A
Rigid control Exit state, 2
p , T , H , S , volume p , T , H , S ,
Inlet state, 1 T
W W
Q
W
E R
Q
p , T
Environment
(b) p p
1 2
Temperature, T 1 b
a
Environment at T and p 0
0
2
Entropy, S
FIGURE P4.2
(a) Schematic diagram of system (b) T-s diagram of processes.