Page 131 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 131
5.6 PROBLEMS 117
system b system a
3 W Turbine
Turbine
Boiler 4
Q
Condenser
Q out W net
1 Feedpump
2
W
Feedpump
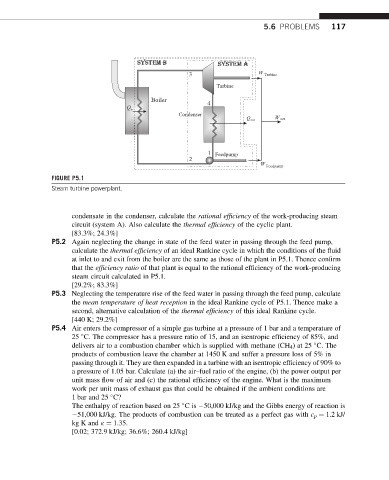
FIGURE P5.1
Steam turbine powerplant.
condensate in the condenser, calculate the rational efficiency of the work-producing steam
circuit (system A). Also calculate the thermal efficiency of the cyclic plant.
[83.3%; 24.3%]
P5.2 Again neglecting the change in state of the feed water in passing through the feed pump,
calculate the thermal efficiency of an ideal Rankine cycle in which the conditions of the fluid
at inlet to and exit from the boiler are the same as those of the plant in P5.1. Thence confirm
that the efficiency ratio of that plant is equal to the rational efficiency of the work-producing
steam circuit calculated in P5.1.
[29.2%; 83.3%]
P5.3 Neglecting the temperature rise of the feed water in passing through the feed pump, calculate
the mean temperature of heat reception in the ideal Rankine cycle of P5.1. Thence make a
second, alternative calculation of the thermal efficiency of this ideal Rankine cycle.
[440 K; 29.2%]
P5.4 Air enters the compressor of a simple gas turbine at a pressure of 1 bar and a temperature of
25 C. The compressor has a pressure ratio of 15, and an isentropic efficiency of 85%, and
delivers air to a combustion chamber which is supplied with methane (CH 4 )at25 C. The
products of combustion leave the chamber at 1450 K and suffer a pressure loss of 5% in
passing through it. They are then expanded in a turbine with an isentropic efficiency of 90% to
a pressure of 1.05 bar. Calculate (a) the air–fuel ratio of the engine, (b) the power output per
unit mass flow of air and (c) the rational efficiency of the engine. What is the maximum
work per unit mass of exhaust gas that could be obtained if the ambient conditions are
1 bar and 25 C?
The enthalpy of reaction based on 25 Cis 50,000 kJ/kg and the Gibbs energy of reaction is
51,000 kJ/kg. The products of combustion can be treated as a perfect gas with c p ¼ 1.2 kJ/
kg K and k ¼ 1.35.
[0.02; 372.9 kJ/kg; 36.6%; 260.4 kJ/kg]