Page 327 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 327
316 CHAPTER 14 CHEMICAL KINETICS
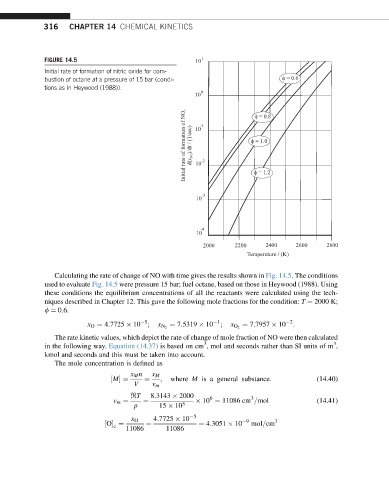
FIGURE 14.5
Initial rate of formation of nitric oxide for com-
bustion of octane at a pressure of 15 bar (condi-
tions as in Heywood (1988)).
Calculating the rate of change of NO with time gives the results shown in Fig. 14.5. The conditions
used to evaluate Fig. 14.5 were pressure 15 bar; fuel octane, based on those in Heywood (1988). Using
these conditions the equilibrium concentrations of all the reactants were calculated using the tech-
niques described in Chapter 12. This gave the following mole fractions for the condition: T ¼ 2000 K;
f ¼ 0.6.
x O ¼ 4:7725 10 5 ; x N 2 ¼ 7:5319 10 1 ; x O 2 ¼ 7:7957 10 2 :
The rate kinetic values, which depict the rate of change of mole fraction of NO were then calculated
3
3
in the following way. Equation (14.37) is based on cm , mol and seconds rather than SI units of m ,
kmol and seconds and this must be taken into account.
The mole concentration is defined as
x M n x M
½M¼ ¼ ; where M is a general substance: (14.40)
V v m
RT 8:3143 2000 6 3
v m ¼ ¼ 5 10 ¼ 11086 cm =mol (14.41)
p 15 10
x O 4:7725 10 5 9 3
½O ¼ 11086 ¼ 11086 ¼ 4:3051 10 mol=cm
e