Page 119 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 119
100 Advanced Mine Ventilation
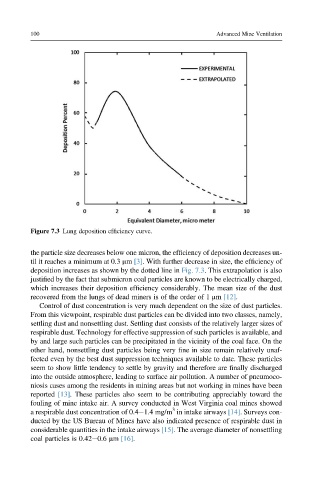
Figure 7.3 Lung deposition efficiency curve.
the particle size decreases below one micron, the efficiency of deposition decreases un-
til it reaches a minimum at 0.3 mm [3]. With further decrease in size, the efficiency of
deposition increases as shown by the dotted line in Fig. 7.3. This extrapolation is also
justified by the fact that submicron coal particles are known to be electrically charged,
which increases their deposition efficiency considerably. The mean size of the dust
recovered from the lungs of dead miners is of the order of 1 mm [12].
Control of dust concentration is very much dependent on the size of dust particles.
From this viewpoint, respirable dust particles can be divided into two classes, namely,
settling dust and nonsettling dust. Settling dust consists of the relatively larger sizes of
respirable dust. Technology for effective suppression of such particles is available, and
by and large such particles can be precipitated in the vicinity of the coal face. On the
other hand, nonsettling dust particles being very fine in size remain relatively unaf-
fected even by the best dust suppression techniques available to date. These particles
seem to show little tendency to settle by gravity and therefore are finally discharged
into the outside atmosphere, leading to surface air pollution. A number of pneumoco-
niosis cases among the residents in mining areas but not working in mines have been
reported [13]. These particles also seem to be contributing appreciably toward the
fouling of mine intake air. A survey conducted in West Virginia coal mines showed
3
a respirable dust concentration of 0.4e1.4 mg/m in intake airways [14]. Surveys con-
ducted by the US Bureau of Mines have also indicated presence of respirable dust in
considerable quantities in the intake airways [15]. The average diameter of nonsettling
coal particles is 0.42e0.6 mm [16].