Page 128 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 128
Characteristics of Respirable Coal Dust Particles 109
Most accepted values of A, Q, and b are 0.879, 0.23, and 2.61, respectively [2].
[ [ b$ r
1þA þQ e [
r r
The term is called mobility of the particle, B such that:
6phr
Fm$B ¼ v (8.10)
Fuchs [2] makes a recommendation for the use of various equations depending on
the particle size to obtain better accuracy (Table 8.2).
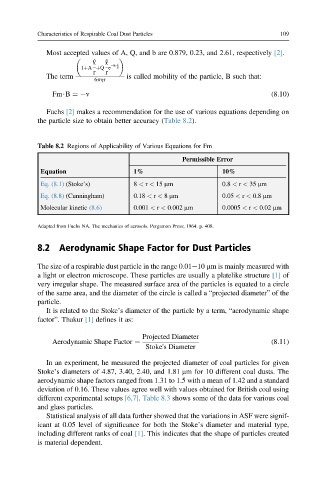
Table 8.2 Regions of Applicability of Various Equations for Fm
Permissible Error
Equation 1% 10%
Eq. (8.1) (Stoke’s) 8 < r < 15 mm 0.8 < r < 35 mm
Eq. (8.8) (Cunningham) 0.18 < r < 8 mm 0.05 < r < 0.8 mm
Molecular kinetic (8.6) 0.001 < r < 0.002 mm 0.0005 < r < 0.02 mm
Adapted from Fuchs NA. The mechanics of aerosols. Pergamon Press; 1964. p. 408.
8.2 Aerodynamic Shape Factor for Dust Particles
The size of a respirable dust particle in the range 0.01e10 mm is mainly measured with
a light or electron microscope. These particles are usually a platelike structure [1] of
very irregular shape. The measured surface area of the particles is equated to a circle
of the same area, and the diameter of the circle is called a “projected diameter” of the
particle.
It is related to the Stoke’s diameter of the particle by a term, “aerodynamic shape
factor”. Thakur [1] defines it as:
Projected Diameter
Aerodynamic Shape Factor ¼ (8.11)
Stoke's Diameter
In an experiment, he measured the projected diameter of coal particles for given
Stoke’s diameters of 4.87, 3.40, 2.40, and 1.81 mm for 10 different coal dusts. The
aerodynamic shape factors ranged from 1.31 to 1.5 with a mean of 1.42 and a standard
deviation of 0.16. These values agree well with values obtained for British coal using
different experimental setups [6,7]. Table 8.3 shows some of the data for various coal
and glass particles.
Statistical analysis of all data further showed that the variations in ASF were signif-
icant at 0.05 level of significance for both the Stoke’s diameter and material type,
including different ranks of coal [1]. This indicates that the shape of particles created
is material dependent.