Page 212 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 212
192 Advanced Mine Ventilation
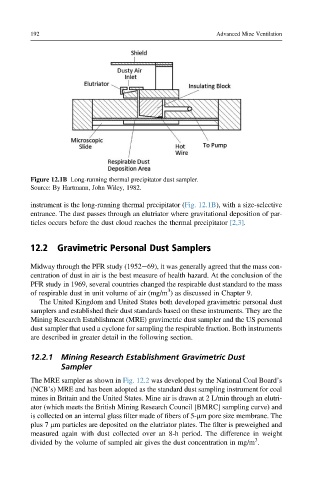
Figure 12.1B Long-running thermal precipitator dust sampler.
Source: By Hartmann, John Wiley, 1982.
instrument is the long-running thermal precipitator (Fig. 12.1B), with a size-selective
entrance. The dust passes through an elutriator where gravitational deposition of par-
ticles occurs before the dust cloud reaches the thermal precipitator [2,3].
12.2 Gravimetric Personal Dust Samplers
Midway through the PFR study (1952e69), it was generally agreed that the mass con-
centration of dust in air is the best measure of health hazard. At the conclusion of the
PFR study in 1969, several countries changed the respirable dust standard to the mass
3
of respirable dust in unit volume of air (mg/m ) as discussed in Chapter 9.
The United Kingdom and United States both developed gravimetric personal dust
samplers and established their dust standards based on these instruments. They are the
Mining Research Establishment (MRE) gravimetric dust sampler and the US personal
dust sampler that used a cyclone for sampling the respirable fraction. Both instruments
are described in greater detail in the following section.
12.2.1 Mining Research Establishment Gravimetric Dust
Sampler
The MRE sampler as shown in Fig. 12.2 was developed by the National Coal Board’s
(NCB’s) MRE and has been adopted as the standard dust sampling instrument for coal
mines in Britain and the United States. Mine air is drawn at 2 L/min through an elutri-
ator (which meets the British Mining Research Council [BMRC] sampling curve) and
is collected on an internal glass filter made of fibers of 5-mm pore size membrane. The
plus 7 mm particles are deposited on the elutriator plates. The filter is preweighed and
measured again with dust collected over an 8-h period. The difference in weight
3
divided by the volume of sampled air gives the dust concentration in mg/m .