Page 218 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 218
198 Advanced Mine Ventilation
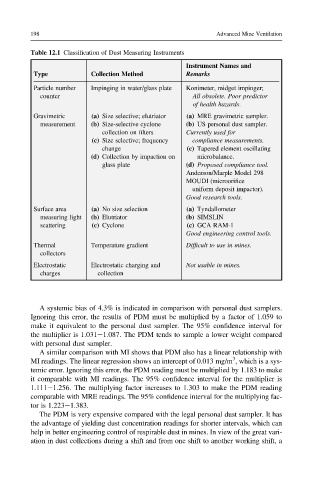
Table 12.1 Classification of Dust Measuring Instruments
Instrument Names and
Remarks
Type Collection Method
Particle number Impinging in water/glass plate Konimeter, midget impinger;
counter All obsolete. Poor predictor
of health hazards.
Gravimetric (a) Size selective; elutriator (a) MRE gravimetric sampler.
measurement (b) Size-selective cyclone (b) US personal dust sampler.
collection on filters Currently used for
(c) Size selective; frequency compliance measurements.
change (c) Tapered element oscillating
(d) Collection by impaction on microbalance.
glass plate (d) Proposed compliance tool.
Anderson/Marple Model 298
MOUDI (microorifice
uniform deposit impactor).
Good research tools.
Surface area (a) No size selection (a) Tyndallometer
measuring light (b) Elutriator (b) SIMSLIN
scattering (c) Cyclone (c) GCA RAM-1
Good engineering control tools.
Thermal Temperature gradient Difficult to use in mines.
collectors
Electrostatic Electrostatic charging and Not usable in mines.
charges collection
A systemic bias of 4.3% is indicated in comparison with personal dust samplers.
Ignoring this error, the results of PDM must be multiplied by a factor of 1.059 to
make it equivalent to the personal dust sampler. The 95% confidence interval for
the multiplier is 1.031e1.087. The PDM tends to sample a lower weight compared
with personal dust sampler.
A similar comparison with MI shows that PDM also has a linear relationship with
3
MI readings. The linear regression shows an intercept of 0.013 mg/m , which is a sys-
temic error. Ignoring this error, the PDM reading must be multiplied by 1.183 to make
it comparable with MI readings. The 95% confidence interval for the multiplier is
1.111e1.256. The multiplying factor increases to 1.303 to make the PDM reading
comparable with MRE readings. The 95% confidence interval for the multiplying fac-
tor is 1.223e1.383.
The PDM is very expensive compared with the legal personal dust sampler. It has
the advantage of yielding dust concentration readings for shorter intervals, which can
help in better engineering control of respirable dust in mines. In view of the great vari-
ation in dust collections during a shift and from one shift to another working shift, a