Page 221 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 221
Respirable Dust Sampling and Measurement 201
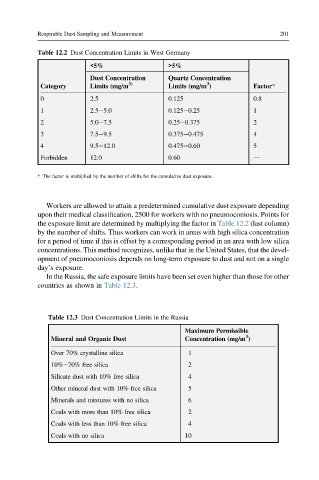
Table 12.2 Dust Concentration Limits in West Germany
<5% >5%
Dust Concentration Quartz Concentration
3) 3
Category Limits (mg/m Limits (mg/m ) Factor*
0 2.5 0.125 0.8
1 2.5e5.0 0.125e0.25 1
2 5.0e7.5 0.25e0.375 2
3 7.5e9.5 0.375e0.475 4
4 9.5e12.0 0.475e0.60 5
Forbidden 12.0 0.60 d
* The factor is multiplied by the number of shifts for the cumulative dust exposure.
Workers are allowed to attain a predetermined cumulative dust exposure depending
upon their medical classification, 2500 for workers with no pneumoconiosis. Points for
the exposure limit are determined by multiplying the factor in Table 12.2 (last column)
by the number of shifts. Thus workers can work in areas with high silica concentration
for a period of time if this is offset by a corresponding period in an area with low silica
concentrations. This method recognizes, unlike that in the United States, that the devel-
opment of pneumoconiosis depends on long-term exposure to dust and not on a single
day’s exposure.
In the Russia, the safe exposure limits have been set even higher than those for other
countries as shown in Table 12.3.
Table 12.3 Dust Concentration Limits in the Russia
Maximum Permissible
3
Mineral and Organic Dust Concentration (mg/m )
Over 70% crystalline silica 1
10%e70% free silica 2
Silicate dust with 10% free silica 4
Other mineral dust with 10% free silica 5
Minerals and mixtures with no silica 6
Coals with more than 10% free silica 2
Coals with less than 10% free silica 4
Coals with no silica 10