Page 243 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 243
Origin of Gases in Coal Mines 221
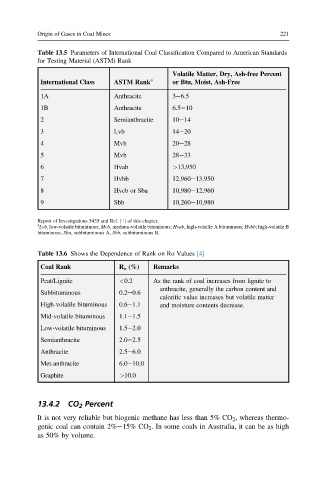
Table 13.5 Parameters of International Coal Classification Compared to American Standards
for Testing Material (ASTM) Rank
Volatile Matter, Dry, Ash-free Percent
a
International Class ASTM Rank or Btu, Moist, Ash-Free
1A Anthracite 3e6.5
1B Anthracite 6.5e10
2 Semianthracite 10e14
3 Lvb 14e20
4 Mvb 20e28
5 Mvb 28e33
6 Hvab >13,950
7 Hvbb 12,960e13,950
8 Hvcb or Sba 10,980e12,960
9 Sbb 10,260e10,980
Report of Investigations 5435 and Ref. [1] of this chapter.
a
Lvb, low-volatile bituminous; Mvb, medium-volatile bituminous; Hvab, high-volatile A bituminous; Hvbb; high-volatile B
bituminous, Sba, subbituminous A, Sbb, subbituminous B.
Table 13.6 Shows the Dependence of Rank on Ro Values [4]
Coal Rank R o (%) Remarks
Peat/Lignite <0.2 As the rank of coal increases from lignite to
anthracite, generally the carbon content and
Subbituminous 0.2e0.6
calorific value increases but volatile matter
High-volatile bituminous 0.6e1.1 and moisture contents decrease.
Mid-volatile bituminous 1.1e1.5
Low-volatile bituminous 1.5e2.0
Semianthracite 2.0e2.5
Anthracite 2.5e6.0
Met-anthracite 6.0e10.0
Graphite >10.0
13.4.2 CO 2 Percent
It is not very reliable but biogenic methane has less than 5% CO 2 , whereas thermo-
genic coal can contain 2%e15% CO 2 . In some coals in Australia, it can be as high
as 50% by volume.