Page 245 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 245
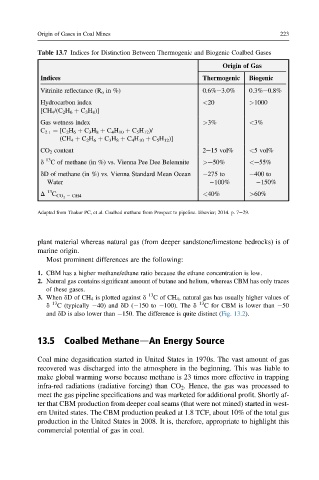
Origin of Gases in Coal Mines 223
Table 13.7 Indices for Distinction Between Thermogenic and Biogenic Coalbed Gases
Origin of Gas
Indices Thermogenic Biogenic
Vitrinite reflectance (R o in %) 0.6%e3.0% 0.3%e0.8%
Hydrocarbon index <20 >1000
[CH 4 /(C 2 H 6 þ C 3 H 8 )]
Gas wetness index >3% <3%
C 2þ ¼ [C 2 H 6 þ C 3 H 8 þ C 4 H 10 þ C 5 H 12 )/
(CH 4 þ C 2 H 6 þ C 3 H 8 þ C 4 H 10 þ C 5 H 12 )]
CO 2 content 2e15 vol% <5 vol%
d 13 C of methane (in %) vs. Vienna Pee Dee Belemnite >e50% <e55%
dD of methane (in %) vs. Vienna Standard Mean Ocean 275 to 400 to
Water 100% 150%
D 13 C CO 2 e CH4 <40% >60%
Adapted from Thakur PC, et al. Coalbed methane from Prospect to pipeline. Elsevier; 2014. p. 7e29.
plant material whereas natural gas (from deeper sandstone/limestone bedrocks) is of
marine origin.
Most prominent differences are the following:
1. CBM has a higher methane/ethane ratio because the ethane concentration is low.
2. Natural gas contains significant amount of butane and helium, whereas CBM has only traces
of these gases.
3. When dDofCH 4 is plotted against d 13 Cof CH 4 , natural gas has usually higher values of
d 13 C (typically 40) and dD( 150 to 100). The d 13 C for CBM is lower than 50
and dD is also lower than 150. The difference is quite distinct (Fig. 13.2).
13.5 Coalbed MethanedAn Energy Source
Coal mine degasification started in United States in 1970s. The vast amount of gas
recovered was discharged into the atmosphere in the beginning. This was liable to
make global warming worse because methane is 23 times more effective in trapping
infra-red radiations (radiative forcing) than CO 2 . Hence, the gas was processed to
meet the gas pipeline specifications and was marketed for additional profit. Shortly af-
ter that CBM production from deeper coal seams (that were not mined) started in west-
ern United states. The CBM production peaked at 1.8 TCF, about 10% of the total gas
production in the United States in 2008. It is, therefore, appropriate to highlight this
commercial potential of gas in coal.