Page 295 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 295
272 Advanced Mine Ventilation
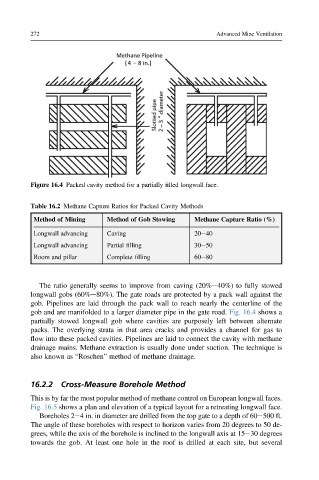
Figure 16.4 Packed cavity method for a partially filled longwall face.
Table 16.2 Methane Capture Ratios for Packed Cavity Methods
Method of Mining Method of Gob Stowing Methane Capture Ratio (%)
Longwall advancing Caving 20e40
Longwall advancing Partial filling 30e50
Room and pillar Complete filling 60e80
The ratio generally seems to improve from caving (20%e40%) to fully stowed
longwall gobs (60%e80%). The gate roads are protected by a pack wall against the
gob. Pipelines are laid through the pack wall to reach nearly the centerline of the
gob and are manifolded to a larger diameter pipe in the gate road. Fig. 16.4 shows a
partially stowed longwall gob where cavities are purposely left between alternate
packs. The overlying strata in that area cracks and provides a channel for gas to
flow into these packed cavities. Pipelines are laid to connect the cavity with methane
drainage mains. Methane extraction is usually done under suction. The technique is
also known as “Roschen” method of methane drainage.
16.2.2 Cross-Measure Borehole Method
This is by far the most popular method of methane control on European longwall faces.
Fig. 16.5 shows a plan and elevation of a typical layout for a retreating longwall face.
Boreholes 2e4 in. in diameter are drilled from the top gate to a depth of 60e500 ft.
The angle of these boreholes with respect to horizon varies from 20 degrees to 50 de-
grees, while the axis of the borehole is inclined to the longwall axis at 15e30 degrees
towards the gob. At least one hole in the roof is drilled at each site, but several