Page 50 - Advances In Productive, Safe, and Responsible Coal Mining
P. 50
36 Advances in Productive, Safe, and Responsible Coal Mining
3.3 Coal-mining history
The history of underground coal mining suggests it is one of the most at-risk mining
sectors and arguably one of the most dangerous industries in human history. It is
among the most inherently hazardous of all commodities mined in the world. Many
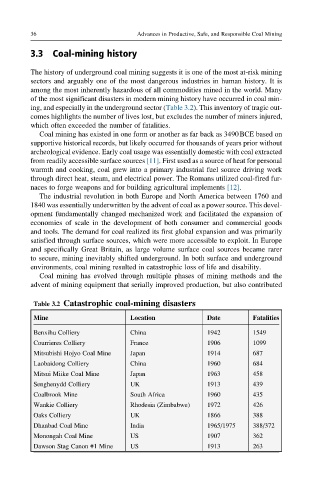
of the most significant disasters in modern mining history have occurred in coal min-
ing, and especially in the underground sector (Table 3.2). This inventory of tragic out-
comes highlights the number of lives lost, but excludes the number of miners injured,
which often exceeded the number of fatalities.
Coal mining has existed in one form or another as far back as 3490BCE based on
supportive historical records, but likely occurred for thousands of years prior without
archeological evidence. Early coal usage was essentially domestic with coal extracted
from readily accessible surface sources [11]. First used as a source of heat for personal
warmth and cooking, coal grew into a primary industrial fuel source driving work
through direct heat, steam, and electrical power. The Romans utilized coal-fired fur-
naces to forge weapons and for building agricultural implements [12].
The industrial revolution in both Europe and North America between 1760 and
1840 was essentially underwritten by the advent of coal as a power source. This devel-
opment fundamentally changed mechanized work and facilitated the expansion of
economies of scale in the development of both consumer and commercial goods
and tools. The demand for coal realized its first global expansion and was primarily
satisfied through surface sources, which were more accessible to exploit. In Europe
and specifically Great Britain, as large volume surface coal sources became rarer
to secure, mining inevitably shifted underground. In both surface and underground
environments, coal mining resulted in catastrophic loss of life and disability.
Coal mining has evolved through multiple phases of mining methods and the
advent of mining equipment that serially improved production, but also contributed
Table 3.2 Catastrophic coal-mining disasters
Mine Location Date Fatalities
Benxihu Colliery China 1942 1549
Courrieres Colliery France 1906 1099
Mitsubishi Hojyo Coal Mine Japan 1914 687
Laobaidong Colliery China 1960 684
Mitsui Miike Coal Mine Japan 1963 458
Senghenydd Colliery UK 1913 439
Coalbrook Mine South Africa 1960 435
Wankie Colliery Rhodesia (Zimbabwe) 1972 426
Oaks Colliery UK 1866 388
Dhanbad Coal Mine India 1965/1975 388/372
Monongah Coal Mine US 1907 362
Dawson Stag Canon #1 Mine US 1913 263