Page 211 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 211
Anaerobic digestion of various feedstocks for second-generation biofuel production 175
Methane
Conventional catalytic Homogeneous radical gas
processing
processes phase reaction
method:
oxidation
process Plasma technologies
Low temperature
homogeneous catalyst
Photo-catalytic
Conversions technologies
technologies Homogeneous catalyst in
solution
Supercritical water
oxidation technologies
Bio catalyst based on
Membrane enzymes
Yielding
technologies
production:
methanol Fuel cell
Other
technologies
Electro-synthesis
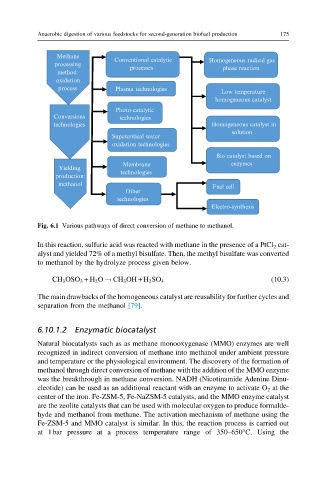
Fig. 6.1 Various pathways of direct conversion of methane to methanol.
In this reaction, sulfuric acid was reacted with methane in the presence of a PtCl 2 cat-
alyst and yielded 72% of a methyl bisulfate. Then, the methyl bisulfate was converted
to methanol by the hydrolyze process given below.
CH 3 OSO 3 +H 2 O ! CH 3 OH + H 2 SO 4 (10.3)
The main drawbacks of the homogeneous catalyst are reusability for further cycles and
separation from the methanol [79].
6.10.1.2 Enzymatic biocatalyst
Natural biocatalysts such as as methane monooxygenase (MMO) enzymes are well
recognized in indirect conversion of methane into methanol under ambient pressure
and temperature or the physiological environment. The discovery of the formation of
methanol through direct conversion of methane with the addition of the MMO enzyme
was the breakthrough in methane conversion. NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinu-
cleotide) can be used as an additional reactant with an enzyme to activate O 2 at the
center of the iron. Fe-ZSM-5, Fe-NaZSM-5 catalysts, and the MMO enzyme catalyst
are the zeolite catalysts that can be used with molecular oxygen to produce formalde-
hyde and methanol from methane. The activation mechanism of methane using the
Fe-ZSM-5 and MMO catalyst is similar. In this, the reaction process is carried out
at 1bar pressure at a process temperature range of 350–650°C. Using the