Page 384 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 384
Ecofuel and its compatibility with different automotive metals to assess diesel engine durability 339
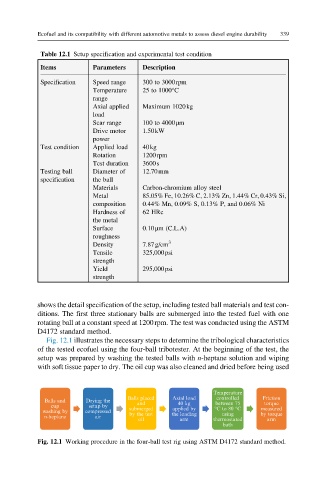
Table 12.1 Setup specification and experimental test condition
Items Parameters Description
Specification Speed range 300 to 3000rpm
Temperature 25 to 1000°C
range
Axial applied Maximum 1020kg
load
Scar range 100 to 4000μm
Drive motor 1.50kW
power
Test condition Applied load 40kg
Rotation 1200rpm
Test duration 3600s
Testing ball Diameter of 12.70mm
specification the ball
Materials Carbon-chromium alloy steel
Metal 85.05% Fe, 10.26% C, 2.13% Zn, 1.44% Cr, 0.43% Si,
composition 0.44% Mn, 0.09% S, 0.13% P, and 0.06% Ni
Hardness of 62 HRc
the metal
Surface 0.10μm (C.L.A)
roughness
Density 7.87g/cm 3
Tensile 325,000psi
strength
Yield 295,000psi
strength
shows the detail specification of the setup, including tested ball materials and test con-
ditions. The first three stationary balls are submerged into the tested fuel with one
rotating ball at a constant speed at 1200rpm. The test was conducted using the ASTM
D4172 standard method.
Fig. 12.1 illustrates the necessary steps to determine the tribological characteristics
of the tested ecofuel using the four-ball tribotester. At the beginning of the test, the
setup was prepared by washing the tested balls with n-heptane solution and wiping
with soft tissue paper to dry. The oil cup was also cleaned and dried before being used
Temperature
Balls placed Axial load controlled Friction
Balls and Drying the
cup setup by and 40 kg between 75 torque
applied by
measured
washing by compressed submerged the loading °C to 80 °C by torque
using
by the test
n-heptane air
oil arm thermostated arm
bath
Fig. 12.1 Working procedure in the four-ball test rig using ASTM D4172 standard method.