Page 261 - Advances in Forensic Applications of Mass Spectrometry - Jehuda Yinon
P. 261
1522_book.fm Page 234 Thursday, November 13, 2003 9:58 AM
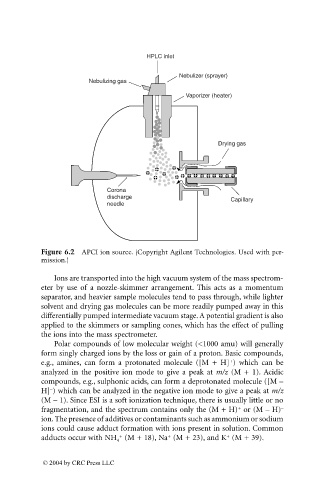
HPLC inlet
Nebulizer (sprayer)
Nebulizing gas
Vaporizer (heater)
Drying gas
Corona
discharge Capillary
needle
Figure 6.2 APCI ion source. (Copyright Agilent Technologies. Used with per-
mission.)
Ions are transported into the high vacuum system of the mass spectrom-
eter by use of a nozzle-skimmer arrangement. This acts as a momentum
separator, and heavier sample molecules tend to pass through, while lighter
solvent and drying gas molecules can be more readily pumped away in this
differentially pumped intermediate vacuum stage. A potential gradient is also
applied to the skimmers or sampling cones, which has the effect of pulling
the ions into the mass spectrometer.
Polar compounds of low molecular weight (<1000 amu) will generally
form singly charged ions by the loss or gain of a proton. Basic compounds,
+
e.g., amines, can form a protonated molecule ([M + H] ) which can be
analyzed in the positive ion mode to give a peak at m/z (M + 1). Acidic
compounds, e.g., sulphonic acids, can form a deprotonated molecule ([M –
–
H] ) which can be analyzed in the negative ion mode to give a peak at m/z
(M – 1). Since ESI is a soft ionization technique, there is usually little or no
+
fragmentation, and the spectrum contains only the (M + H) or (M – H) –
ion. The presence of additives or contaminants such as ammonium or sodium
ions could cause adduct formation with ions present in solution. Common
+
+
+
adducts occur with NH (M + 18), Na (M + 23), and K (M + 39).
4
© 2004 by CRC Press LLC