Page 239 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 239
212 CHAPTER 6 Flexible Power Control of Photovoltaic Systems
A compromise of this solution is the extra cost because of the ESS. Although the
cost of battery is continuously decreasing, the total cost of PV systems with inte-
grating ESS is still considerably higher than the conventional PV systems [26].
This is mainly because of the cost of extra equipment such as batteries and battery
management systems and also the operation and maintenance costs. With the recent
technology, the warranty period of the commercial battery (e.g., lithium ion) is usu-
ally limited to less than 5 year [27], whereas the typical PV systems are expected to
last for 20e30 years. When looking from the reliability perspective, although the
ESSs provide the flexibility in power injection of the PV systems, they also introduce
other possible failure mechanisms in the overall PV systems.
3.2 INSTALLING FLEXIBLE LOADS
Another solution to provide the power control flexibility through extra equipment is
by installing flexible loads locally. The main idea of this approach is to absorb the
surplus PV energy through the demand side management, where the flexibility is
provided by the load that absorbs the surplus PVenergy locally [24]. The basic con-
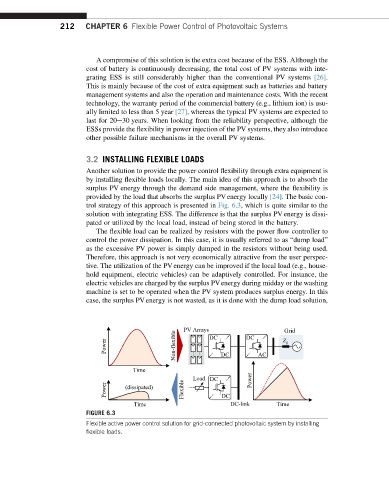
trol strategy of this approach is presented in Fig. 6.3, which is quite similar to the
solution with integrating ESS. The difference is that the surplus PV energy is dissi-
pated or utilized by the local load, instead of being stored in the battery.
The flexible load can be realized by resistors with the power flow controller to
control the power dissipation. In this case, it is usually referred to as “dump load”
as the excessive PV power is simply dumped in the resistors without being used.
Therefore, this approach is not very economically attractive from the user perspec-
tive. The utilization of the PV energy can be improved if the local load (e.g., house-
hold equipment, electric vehicles) can be adaptively controlled. For instance, the
electric vehicles are charged by the surplus PVenergy during midday or the washing
machine is set to be operated when the PV system produces surplus energy. In this
case, the surplus PV energy is not wasted, as it is done with the dump load solution,
FIGURE 6.3
Flexible active power control solution for grid-connected photovoltaic system by installing
flexible loads.