Page 121 - Advances in Textile Biotechnology
P. 121
102 Advances in textile biotechnology
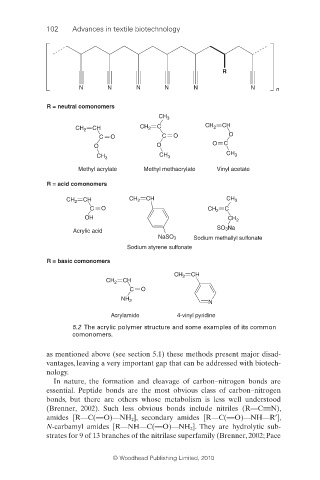
R
N N N N N N n
R = neutral comonomers
CH 3
CH 2 CH CH 2 C CH 2 CH
C O C O O
O O O C
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
Methyl acrylate Methyl methacrylate Vinyl acetate
R = acid comonomers
CH CH CH
CH 2 CH 2 3
C O CH 2 C
OH CH 2
SO 3Na
Acrylic acid
NaSO 3 Sodium methallyl sulfonate
Sodium styrene sulfonate
R = basic comonomers
CH 2 CH
CH 2 CH
C O
NH 2 N
Acrylamide 4-vinyl pyridine
5.2 The acrylic polymer structure and some examples of its common
comonomers.
as mentioned above (see section 5.1) these methods present major disad-
vantages, leaving a very important gap that can be addressed with biotech-
nology.
In nature, the formation and cleavage of carbon–nitrogen bonds are
essential. Peptide bonds are the most obvious class of carbon–nitrogen
bonds, but there are others whose metabolism is less well understood
(Brenner, 2002). Such less obvious bonds include nitriles (R—C≡N),
amides [R—C(=O)—NH 2 ], secondary amides [R—C(=O)—NH—R′],
N-carbamyl amides [R—NH—C(=O)—NH 2 ]. They are hydrolytic sub-
strates for 9 of 13 branches of the nitrilase superfamily (Brenner, 2002; Pace
© Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2010