Page 125 - Advances in Textile Biotechnology
P. 125
106 Advances in textile biotechnology
OCOCH 3 OCOCH 3
OCOCH 3 OCOCH 3
O H 3 COCO O H 3 COCO
O O O
H 3 COCO O H 3 COCO O
O O
OCOCH 3 OCOCH 3
H 3 COCO H 3 COCO
H 2O
Acetyl esterases
(EC 3.1) CH 3COOH
OCOCH 3 OCOCH 3
OH
O HO O HO OCOCH 3
O O O
HO O HO O
O O
OH OH
H 3 COCO H 3 COCO
H 2 O
Endoglucanases
OCOCH 3
OCOCH 3
O OH OCOCH 3
O OH HO O O HO O
HO HO HO O
OH O OH O
H 3 COCO H 3 COCO
H 2 O
OCOCH 3 Exoglucanases
OH OCOCH 3
HO O HO
O O
HO HO OH HO
O O
OH
H 3 COCO H 3 COCO
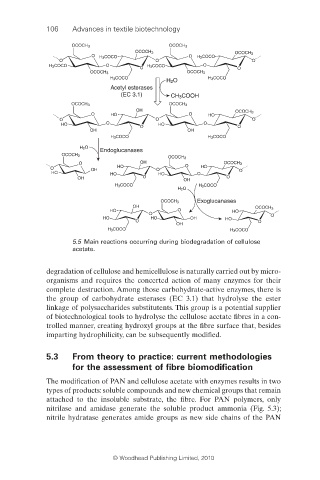
5.5 Main reactions occurring during biodegradation of cellulose
acetate.
degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose is naturally carried out by micro-
organisms and requires the concerted action of many enzymes for their
complete destruction. Among those carbohydrate-active enzymes, there is
the group of carbohydrate esterases (EC 3.1) that hydrolyse the ester
linkage of polysaccharides substitutents. This group is a potential supplier
of biotechnological tools to hydrolyse the cellulose acetate fibres in a con-
trolled manner, creating hydroxyl groups at the fibre surface that, besides
imparting hydrophilicity, can be subsequently modifi ed.
5.3 From theory to practice: current methodologies
for the assessment of fi bre biomodifi cation
The modification of PAN and cellulose acetate with enzymes results in two
types of products: soluble compounds and new chemical groups that remain
attached to the insoluble substrate, the fibre. For PAN polymers, only
nitrilase and amidase generate the soluble product ammonia (Fig. 5.3);
nitrile hydratase generates amide groups as new side chains of the PAN
© Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2010