Page 132 - Advances in Textile Biotechnology
P. 132
Enzymatic modifi cation of polyacrylonitrile and cellulose acetate fi bres 113
fabrics treated with nitrilase without additives). Further assays without
additives were performed to study the progression of the modifi cation of
PAN catalysed by nitrilase over a maximum period of 36 h, at 40 °C and pH
7.8. The conversion of nitrile groups into carboxylic groups was followed
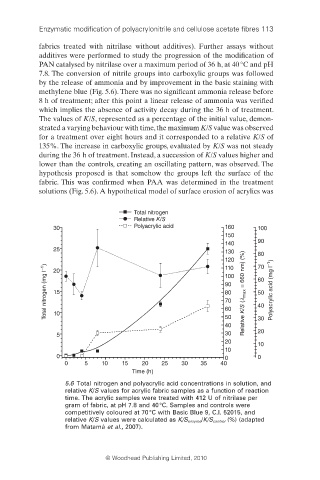
by the release of ammonia and by improvement in the basic staining with
methylene blue (Fig. 5.6). There was no significant ammonia release before
8 h of treatment; after this point a linear release of ammonia was verifi ed
which implies the absence of activity decay during the 36 h of treatment.
The values of K/S, represented as a percentage of the initial value, demon-
strated a varying behaviour with time, the maximum K/S value was observed
for a treatment over eight hours and it corresponded to a relative K/S of
135%. The increase in carboxylic groups, evaluated by K/S was not steady
during the 36 h of treatment. Instead, a succession of K/S values higher and
lower than the controls, creating an oscillating pattern, was observed. The
hypothesis proposed is that somehow the groups left the surface of the
fabric. This was confirmed when PAA was determined in the treatment
solutions (Fig. 5.6). A hypothetical model of surface erosion of acrylics was
Total nitrogen
Relative K/S
30 Polyacrylic acid 160 100
150
90
140
25 130 80
120 70
Total nitrogen (mg l –1 ) 15 100 Relative K/S (l max = 660 nm) (%) 60 Polyacrylic acid (mg l –1 )
110
20
90
80
50
70
40
60
10
50
40 30
5 30 20
20
10
10
0 0 0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Time (h)
5.6 Total nitrogen and polyacrylic acid concentrations in solution, and
relative K/S values for acrylic fabric samples as a function of reaction
time. The acrylic samples were treated with 412 U of nitrilase per
gram of fabric, at pH 7.8 and 40 °C. Samples and controls were
competitively coloured at 70 °C with Basic Blue 9, C.I. 52015, and
relative K/S values were calculated as K/S enzyme/K/S control (%) (adapted
from Matamá et al., 2007).
© Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2010