Page 135 - Advances in Textile Biotechnology
P. 135
References Tauber et al. (2000) Battistel et al. (2001) Wang et al. (2004)
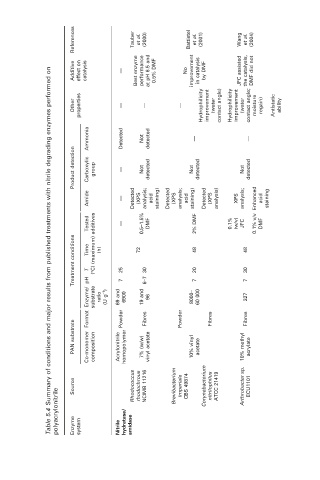
Additive effect on catalysis — Best enzyme performance at pH 6.5 and 0.5% DMF No improvement in catalysis by DMF JFC assisted DMF did not
Table 5.4 Summary of conditions and major results from published treatments with nitrile degrading enzymes performed on
Other properties — — — Hydrophilicity improvement (water contact angle) Hydrophilicity improvement (water contact angle; the catalysis, moisture regain) Antistatic ability
Ammonia Detected Not detected — —
Product detection Carboxylic group — Not detected Not detected Not detected
Amide — Detected (XPS analysis; acid staining) Detected (XPS analysis; acid staining) Detected (XPS analysis) XPS analysis; Enhanced acid staining
Tested (maximum) additives — 0.5–1.5% DMF 2% DMF 0.1% (w/v) JFC 0.1% v/v DMF
Treatment conditions Time T (°C) (h) 25 72 30 48 20 48 30
Enzyme/ pH substrate ratio (U g −1 ) 69 and 7 6900 19 and 6–7 96 8000– 7 60 000 7 327
Format Powder Fibres Powder Fibres Fibres
PAN substrate Co-monomer composition Acrylonitrile homopolymer 7% (w/w) vinyl acetate 10% vinyl acetate 10% methyl acrylate
Source Rhodococcus rhodochrous NCIMB 11216 Brevibacterium imperiale CBS 49874 Corynebacterium nitrilophilus ATCC 21419 Arthrobacter sp. ECU1101
polyacrylonitrile Enzyme system Nitrile hydratase/ amidase