Page 153 - Advances in Textile Biotechnology
P. 153
134 Advances in textile biotechnology
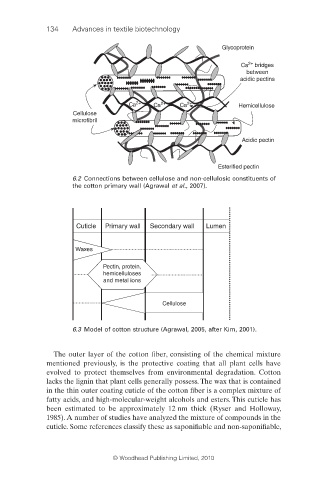
Glycoprotein
2+
Ca bridges
between
acidic pectins
Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Hemicellulose
Cellulose
microfibril
Acidic pectin
Esterified pectin
6.2 Connections between cellulose and non-cellulosic constituents of
the cotton primary wall (Agrawal et al., 2007).
Cuticle Primary wall Secondary wall Lumen
Waxes
Pectin, protein,
hemicelluloses
and metal ions
Cellulose
6.3 Model of cotton structure (Agrawal, 2005, after Kim, 2001).
The outer layer of the cotton fiber, consisting of the chemical mixture
mentioned previously, is the protective coating that all plant cells have
evolved to protect themselves from environmental degradation. Cotton
lacks the lignin that plant cells generally possess. The wax that is contained
in the thin outer coating cuticle of the cotton fi ber is a complex mixture of
fatty acids, and high-molecular-weight alcohols and esters. This cuticle has
been estimated to be approximately 12 nm thick (Ryser and Holloway,
1985). A number of studies have analyzed the mixture of compounds in the
cuticle. Some references classify these as saponifiable and non-saponifi able,
© Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2010