Page 239 - Advances in Textile Biotechnology
P. 239
220 Advances in textile biotechnology
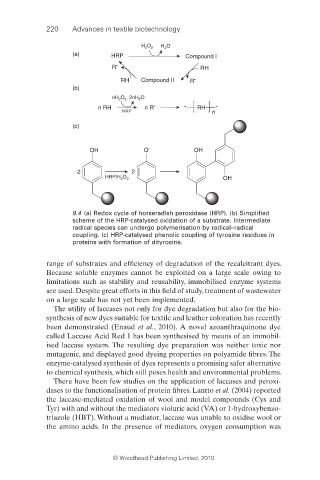
H O H O
2 2 2
(a) HRP Compound I
R • RH
RH Compound II R •
(b)
nH O 2nH O
2
2
2
n RH n R • * RH *
HRP n
(c)
OH O · OH
2 2
HRP/H O 2 OH
2
9.4 (a) Redox cycle of horseradish peroxidase (HRP). (b) Simplifi ed
scheme of the HRP-catalysed oxidation of a substrate. Intermediate
radical species can undergo polymerisation by radical–radical
coupling. (c) HRP-catalysed phenolic coupling of tyrosine residues in
proteins with formation of dityrosine.
range of substrates and efficiency of degradation of the recalcitrant dyes.
Because soluble enzymes cannot be exploited on a large scale owing to
limitations such as stability and reusability, immobilised enzyme systems
are used. Despite great efforts in this field of study, treatment of wastewater
on a large scale has not yet been implemented.
The utility of laccases not only for dye degradation but also for the bio-
synthesis of new dyes suitable for textile and leather coloration has recently
been demonstrated (Enaud et al., 2010). A novel azoanthraquinone dye
called Laccase Acid Red 1 has been synthesised by means of an immobil-
ised laccase system. The resulting dye preparation was neither toxic nor
mutagenic, and displayed good dyeing properties on polyamide fi bres. The
enzyme-catalysed synthesis of dyes represents a promising safer alternative
to chemical synthesis, which still poses health and environmental problems.
There have been few studies on the application of laccases and peroxi-
dases to the functionalisation of protein fi bres. Lantto et al. (2004) reported
the laccase-mediated oxidation of wool and model compounds (Cys and
Tyr) with and without the mediators violuric acid (VA) or 1-hydroxybenzo-
triazole (HBT). Without a mediator, laccase was unable to oxidise wool or
the amino acids. In the presence of mediators, oxygen consumption was
© Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2010