Page 269 - Advances in Textile Biotechnology
P. 269
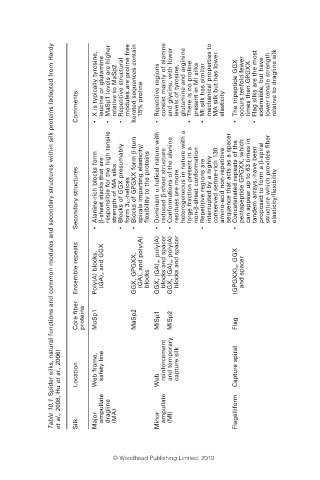
Table 10.1 Spider silks, natural functions and common modules and secondary structures within silk proteins (adapted from Hardy
X is typically tyrosine, leucine or glutamine MaSp1 levels are higher relative to MaSp2 • Repetitive structural modules are proline free Iterated sequences contain • Repetitive regions consist mainly of alanine and glycine, with lower levels of tyrosine, glutamine and arginine There is no proline present in M
Comments • • 15% proline • • elasticity • • ber
Secondary structures Alanine-rich blocks form • β-sheet stacks that are responsible for the high tensile strength of MA silks Blocks of GGX presumably • form 3 10 -helices Blocks of GPGXX form β-turn • spirals imparting elasticity/ flexibility to the proteins • Dominant α-helical nature with reduced β-sheet struc
Ensemble repeats Poly(A) blocks, (GA) n and GGX GGX, GPGXX, (GA) n and poly(A) blocks GGX, (GA) n, poly(A) blocks and spacer GGX, (GA) n, poly(A) blocks and spacer (GPGXX) n , GGX and spacer
ber
Core fi proteins MaSp1 MaSp2 MiSp1 MiSp2 Flag
et al., 2008, Hu et al., 2006) Location Web frame, Major safety line ampullate dragline (MA) Web Minor reinforcement ampullate and temporary (MI) capture silk Capture spiral Flagelliform
Silk
© Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2010