Page 234 - Aerodynamics for Engineering Students
P. 234
Finite wing theory 2 17
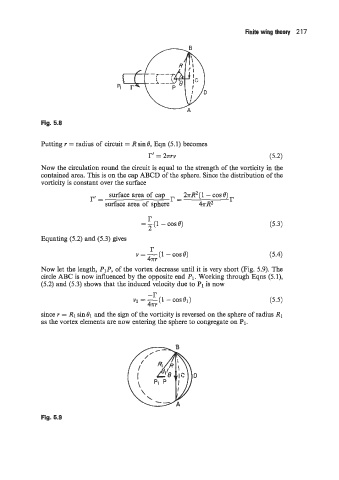
Fig. 5.8
Putting r = radius of circuit = Rsinf3, Eqn (5.1) becomes
rt = 2rrv (54
Now the circulation round the circuit is equal to the strength of the vorticity in the
contained area. This is on the cap ABCD of the sphere. Since the distribution of the
vorticity is constant over the surface
r= surface area of cap 2rR2( 1 - cos 0) r
surface area of spherer = 4rR2
Equating (5.2) and (5.3) gives
Now let the length, PIP, of the vortex decrease until it is very short (Fig. 5.9). The
circle ABC is now influenced by the opposite end PI. Working through Eqns (5.1),
(5.2) and (5.3) shows that the induced velocity due to P1 is now
-r
v1 =-(I -cosel) (5.5)
4m
since I = R1 sin 81 and the sign of the vorticity is reversed on the sphere of radius R1
as the vortex elements are now entering the sphere to congregate on PI.
Fig. 5.9