Page 115 - Aeronautical Engineer Data Book
P. 115
Basic fluid mechanics 91
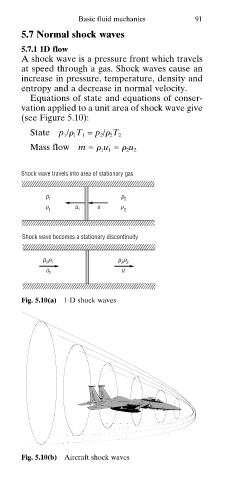
5.7 Normal shock waves
5.7.1 1D flow
A shock wave is a pressure front which travels
at speed through a gas. Shock waves cause an
increase in pressure, temperature, density and
entropy and a decrease in normal velocity.
Equations of state and equations of conser-
vation applied to a unit area of shock wave give
(see Figure 5.10):
/ T = p / T
State p 1 1 1 2 2 2
Mass flow m = u = u
1 1
2 2
Shock wave travels into area of stationary gas
p p
1 2
1 u 1 u 2
Shock wave becomes a stationary discontinuity
p p
1 1 2 2
u 1 u
Fig. 5.10(a) 1-D shock waves
Fig. 5.10(b) Aircraft shock waves