Page 482 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 482
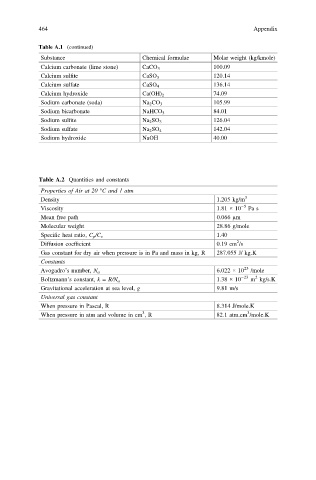
464 Appendix
Table A.1 (continued)
Substance Chemical formulae Molar weight (kg/kmole)
Calcium carbonate (lime stone) CaCO 3 100.09
Calcium sulfite CaSO 3 120.14
Calcium sulfate CaSO 4 136.14
Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH) 2 74.09
Sodium carbonate (soda) Na 2 CO 3 105.99
Sodium bicarbonate NaHCO 3 84.01
Sodium sulfite Na 2 SO 3 126.04
Sodium sulfate Na 2 SO 4 142.04
Sodium hydroxide NaOH 40.00
Table A.2 Quantities and constants
Properties of Air at 20 °C and 1 atm
Density 1.205 kg/m 3
Viscosity 1.81 × 10 −5 Pa s
Mean free path 0.066 μm
Molecular weight 28.86 g/mole
Specific heat ratio, C p /C v 1.40
2
Diffusion coefficient 0.19 cm /s
Gas constant for dry air when pressure is in Pa and mass in kg, R 287.055 J/ kg.K
Constants
Avogadro’s number, N a 6.022 × 10 23 /mole
2
1.38 × 10 −23 m kg/s.K
Boltzmann’s constant, k = R/N a
Gravitational acceleration at sea level, g 9.81 m/s
Universal gas constant
When pressure in Pascal, R 8.314 J/mole.K
3
3
When pressure in atm and volume in cm , R 82.1 atm.cm /mole.K