Page 657 - Air and Gas Drilling Manual
P. 657
Chapter 12: Directional Drilling Operations 12-21
horsepower and 200 rpm). Table 12-2 gives a summary of the pressures as a
function of true vertical depth (TVD) and measured depth (MD).
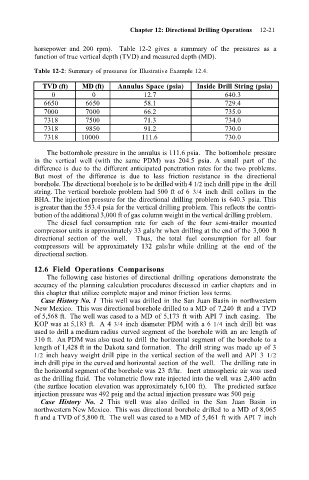
Table 12-2: Summary of pressures for Illustrative Example 12.4.
TVD (ft) MD (ft) Annulus Space (psia) Inside Drill String (psia)
0 0 12.7 640.3
6650 6650 58.1 729.4
7000 7000 66.2 735.0
7318 7500 71.3 734.0
7318 9850 91.2 730.0
7318 10000 111.6 730.0
The bottomhole pressure in the annulus is 111.6 psia. The bottomhole pressure
in the vertical well (with the same PDM) was 204.5 psia. A small part of the
difference is due to the different anticipated penetration rates for the two problems.
But most of the difference is due to less friction resistance in the directional
borehole. The directional borehole is to be drilled with 4 1/2 inch drill pipe in the drill
string. The vertical borehole problem had 500 ft of 6 3/4 inch drill collars in the
BHA. The injection pressure for the directional drilling problem is 640.3 psia. This
is greater than the 553.4 psia for the vertical drilling problem. This reflects the contri-
bution of the additional 3,000 ft of gas column weight in the vertical drilling problem.
The diesel fuel consumption rate for each of the four semi-trailer mounted
compressor units is approximately 33 gals/hr when drilling at the end of the 3,000 ft
directional section of the well. Thus, the total fuel consumption for all four
compressors will be approximately 132 gals/hr while drilling at the end of the
directional section.
12.6 Field Operations Comparisons
The following case histories of directional drilling operations demonstrate the
accuracy of the planning calculation procedures discussed in earlier chapters and in
this chapter that utilize complete major and minor friction loss terms.
Case History No. 1 This well was drilled in the San Juan Basin in northwestern
New Mexico. This was directional borehole drilled to a MD of 7,240 ft and a TVD
of 5,568 ft. The well was cased to a MD of 5,173 ft with API 7 inch casing. The
KOP was at 5,183 ft. A 4 3/4 inch diameter PDM with a 6 1/4 inch drill bit was
used to drill a medium radius curved segment of the borehole with an arc length of
310 ft. An PDM was also used to drill the horizontal segment of the borehole to a
length of 1,428 ft in the Dakota sand formation. The drill string was made up of 3
1/2 inch heavy weight drill pipe in the vertical section of the well and API 3 1/2
inch drill pipe in the curved and horizontal section of the well. The drilling rate in
the horizontal segment of the borehole was 23 ft/hr. Inert atmospheric air was used
as the drilling fluid. The volumetric flow rate injected into the well was 2,400 acfm
(the surface location elevation was approximately 6,100 ft). The predicted surface
injection pressure was 492 psig and the actual injection pressure was 500 psig
Case History No. 2 This well was also drilled in the San Juan Basin in
northwestern New Mexico. This was directional borehole drilled to a MD of 8,065
ft and a TVD of 5,800 ft. The well was cased to a MD of 5,461 ft with API 7 inch