Page 92 - Air and Gas Drilling Manual
P. 92
3-20 Air and Gas Drilling Manual
stabilizer blades in air drilling operations will be greater than in a mud drilling
operation (assuming similar geologic conditions).
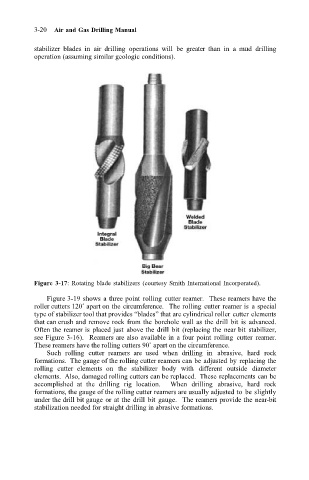
Figure 3-17: Rotating blade stabilizers (courtesy Smith International Incorporated).
Figure 3-19 shows a three point rolling cutter reamer. These reamers have the
roller cutters 120˚ apart on the circumference. The rolling cutter reamer is a special
type of stabilizer tool that provides “blades” that are cylindrical roller cutter elements
that can crush and remove rock from the borehole wall as the drill bit is advanced.
Often the reamer is placed just above the drill bit (replacing the near bit stabilizer,
see Figure 3-16). Reamers are also available in a four point rolling cutter reamer.
These reamers have the rolling cutters 90˚ apart on the circumference.
Such rolling cutter reamers are used when drilling in abrasive, hard rock
formations. The gauge of the rolling cutter reamers can be adjusted by replacing the
rolling cutter elements on the stabilizer body with different outside diameter
elements. Also, damaged rolling cutters can be replaced. These replacements can be
accomplished at the drilling rig location. When drilling abrasive, hard rock
formations, the gauge of the rolling cutter reamers are usually adjusted to be slightly
under the drill bit gauge or at the drill bit gauge. The reamers provide the near-bit
stabilization needed for straight drilling in abrasive formations.