Page 373 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 373
354 Open and closed, thin-walled beams
Assuming that the direct stresses are distributed according to the basic theory of
bending, calculate and sketch the shear flow distribution for a vertical shear force
S,, applied tangentially to the curved part of the beam.
Ans. qol = S,,( 1.61 cos 8 - 0.80)/r
q12 = Sy(0.57SS - 1.14rs - 0.33)/r
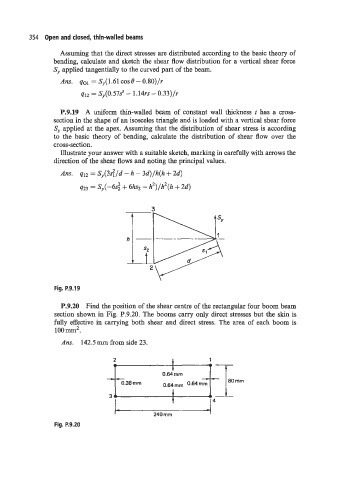
P.9.19 A uniform thin-walled beam of constant wall thickness t has a cross-
section in the shape of an isosceles triangle and is loaded with a vertical shear force
Sy applied at the apex. Assuming that the distribution of shear stress is according
to the basic theory of bending, calculate the distribution of shear flow over the
cross-section.
Illustrate your answer with a suitable sketch, marking in carefully with arrows the
direction of the shear flows and noting the principal values.
Ans. q12 = SY(33/d - h - 3d)/h(h + 2d)
q23 = S,,(-6$ + 6h~2 - h2)/h2(h + 2d)
3
Fig. P.9.19
P.9.20 Find the position of the shear centre of the rectangular four boom beam
section shown in Fig. P.9.20. The booms carry only direct stresses but the skin is
fully effective in carrying both shear and direct stress. The area of each boom is
lO0mm2.
Ans. 142.5 mm from side 23.
3
I 14
I- 240 mm I
Fig. P.9.20