Page 375 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 375
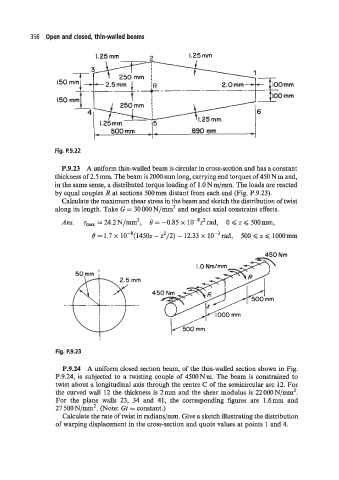
356 Open and closed, thin-walled beams
1.25 mm 3 1.25 mm
r-
1.25 mm
500mm d+ 890 mm
Fig. P.9.22
P.9.23 A uniform thin-walled beam is circular in cross-section and has a constant
thickness of 2.5 mm. The beam is 2000 mm long, carrying end torques of 450 N m and,
in the same sense, a distributed torque loading of 1 .O N m/mm. The loads are reacted
by equal couples R at sections 500 mm distant from each end (Fig. P.9.23).
Calculate the maximum shear stress in the beam and sketch the distribution of twist
along its length. Take G = 30 000 N/mm2 and neglect axial constraint effects.
Am. r,, = 24.2N/mm2, 8 = -0.85 .x 10-82rad, 0 < z < 500mm,
8 = 1.7 x 10-8(1450~ - z2/2) - 12.33 x rad, 500 < z < 1OOOmm
Fig. P.9.23
P.9.24 A uniform closed section beam, of the thin-walled section shown in Fig.
P.9.24, is subjected to a twisting couple of 4500Nm. The beam is constrained to
twist about a longitudinal axis through the centre C of the semicircular arc 12. For
the curved wall 12 the thickness is 2 mm and the shear modulus is 22 000 N/mm2.
For the plane walls 23, 34 and 41, the corresponding figures are 1.6mm and
27 500 N/mm2. (Note: Gt = constant.)
Calculate the rate of twist in radians/mm. Give a sketch illustrating the distribution
of warping displacement in the cross-section and quote values at points 1 and 4.