Page 203 - Algae
P. 203
186 Algae: Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology
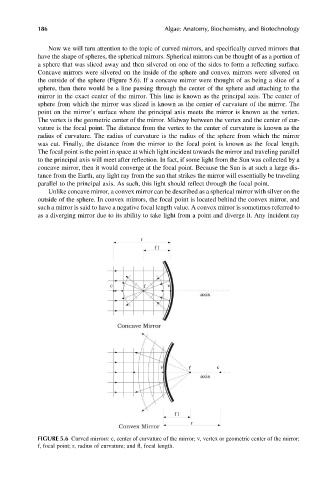
Now we will turn attention to the topic of curved mirrors, and specifically curved mirrors that
have the shape of spheres, the spherical mirrors. Spherical mirrors can be thought of as a portion of
a sphere that was sliced away and then silvered on one of the sides to form a reflecting surface.
Concave mirrors were silvered on the inside of the sphere and convex mirrors were silvered on
the outside of the sphere (Figure 5.6). If a concave mirror were thought of as being a slice of a
sphere, then there would be a line passing through the center of the sphere and attaching to the
mirror in the exact center of the mirror. This line is known as the principal axis. The center of
sphere from which the mirror was sliced is known as the center of curvature of the mirror. The
point on the mirror’s surface where the principal axis meets the mirror is known as the vertex.
The vertex is the geometric center of the mirror. Midway between the vertex and the center of cur-
vature is the focal point. The distance from the vertex to the center of curvature is known as the
radius of curvature. The radius of curvature is the radius of the sphere from which the mirror
was cut. Finally, the distance from the mirror to the focal point is known as the focal length.
The focal point is the point in space at which light incident towards the mirror and traveling parallel
to the principal axis will meet after reflection. In fact, if some light from the Sun was collected by a
concave mirror, then it would converge at the focal point. Because the Sun is at such a large dis-
tance from the Earth, any light ray from the sun that strikes the mirror will essentially be traveling
parallel to the principal axis. As such, this light should reflect through the focal point.
Unlike concave mirror, a convex mirror can be described as a spherical mirror with silver on the
outside of the sphere. In convex mirrors, the focal point is located behind the convex mirror, and
such a mirror is said to have a negative focal length value. A convex mirror is sometimes referred to
as a diverging mirror due to its ability to take light from a point and diverge it. Any incident ray
FIGURE 5.6 Curved mirrors: c, center of curvature of the mirror; v, vertex or geometric center of the mirror;
f, focal point; r, radius of curvature; and fl, focal length.