Page 207 - Algae
P. 207
190 Algae: Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology
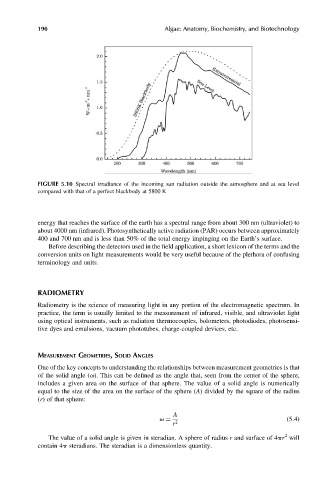
FIGURE 5.10 Spectral irradiance of the incoming sun radiation outside the atmosphere and at sea level
compared with that of a perfect blackbody at 5800 K
energy that reaches the surface of the earth has a spectral range from about 300 nm (ultraviolet) to
about 4000 nm (infrared). Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) occurs between approximately
400 and 700 nm and is less than 50% of the total energy impinging on the Earth’s surface.
Before describing the detectors used in the field application, a short lexicon of the terms and the
conversion units on light measurements would be very useful because of the plethora of confusing
terminology and units.
RADIOMETRY
Radiometry is the science of measuring light in any portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. In
practice, the term is usually limited to the measurement of infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light
using optical instruments, such as radiation thermocouples, bolometers, photodiodes, photosensi-
tive dyes and emulsions, vacuum phototubes, charge-coupled devices, etc.
MEASUREMENT GEOMETRIES,SOLID ANGLES
One of the key concepts to understanding the relationships between measurement geometries is that
of the solid angle (v). This can be defined as the angle that, seen from the center of the sphere,
includes a given area on the surface of that sphere. The value of a solid angle is numerically
equal to the size of the area on the surface of the sphere (A) divided by the square of the radius
(r) of that sphere:
A
v ¼ (5:4)
r 2
2
The value of a solid angle is given in steradian. A sphere of radius r and surface of 4pr will
contain 4p steradians. The steradian is a dimensionless quantity.