Page 83 -
P. 83
Chapter 2 ■ Edge-Detection Techniques 57
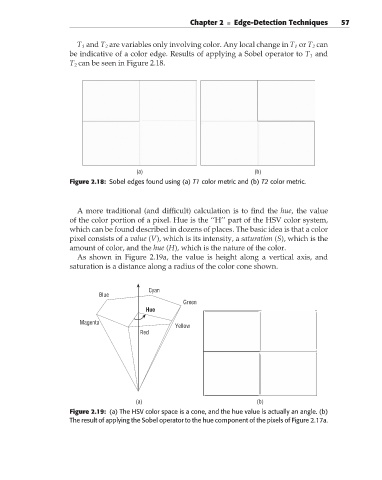
T 1 and T 2 are variables only involving color. Any local change in T 1 or T 2 can
be indicative of a color edge. Results of applying a Sobel operator to T 1 and
T 2 can be seen in Figure 2.18.
(a) (b)
Figure 2.18: Sobel edges found using (a) T1 color metric and (b) T2 color metric.
A more traditional (and difficult) calculation is to find the hue,the value
of the color portion of a pixel. Hue is the ‘‘H’’ part of the HSV color system,
which can be found described in dozens of places. The basic idea is that a color
pixel consists of a value (V), which is its intensity, a saturation (S), which is the
amount of color, and the hue (H), which is the nature of the color.
As shown in Figure 2.19a, the value is height along a vertical axis, and
saturation is a distance along a radius of the color cone shown.
Cyan
Blue
Green
Hue
Magenta
Yellow
Red
(a) (b)
Figure 2.19: (a) The HSV color space is a cone, and the hue value is actually an angle. (b)
The result of applying the Sobel operator to the hue component of the pixels of Figure 2.17a.