Page 52 - Alternative Energy Systems in Building Design
P. 52
SOLAR CELL PHYSICS 29
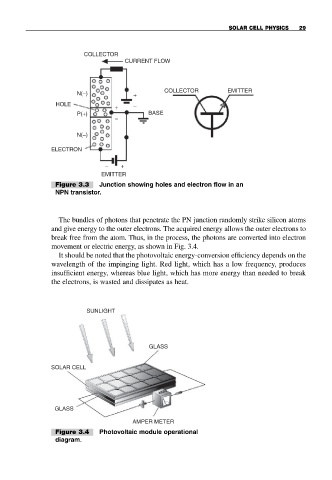
COLLECTOR
CURRENT FLOW
COLLECTOR EMITTER
N(−) +
HOLE
+ −
P(+) BASE
−
N(−)
ELECTRON
− +
EMITTER
Figure 3.3 Junction showing holes and electron flow in an
NPN transistor.
The bundles of photons that penetrate the PN junction randomly strike silicon atoms
and give energy to the outer electrons. The acquired energy allows the outer electrons to
break free from the atom. Thus, in the process, the photons are converted into electron
movement or electric energy, as shown in Fig. 3.4.
It should be noted that the photovoltaic energy-conversion efficiency depends on the
wavelength of the impinging light. Red light, which has a low frequency, produces
insufficient energy, whereas blue light, which has more energy than needed to break
the electrons, is wasted and dissipates as heat.
SUNLIGHT
GLASS
SOLAR CELL
GLASS
AMPER METER
Figure 3.4 Photovoltaic module operational
diagram.