Page 17 - An Introduction to Analytical Atomic Spectrometry - L. Ebdon
P. 17
Page 2
the problems associated with flames, arcs and sparks. The term emission spectroscopy is applied to the
measurement of light emitted from flames or plasmas by chemical species after the absorption of energy
as heat or as chemical energy (i.e. chemiluminescence). If only the emission from atoms is observed,
the term atomic emission spectroscopy is preferred.
Atomic absorption spectroscopy is the term used when the radiation absorbed by atoms is measured.
The application of AAS to analytical problems was considerably delayed because of the apparent need
for very high resolution to make quantitative measurements. In 1953, Walsh brilliantly overcame this
obstacle by the use of a line source, an idea pursued independently by Alkemade, his work being
published in 1955.
The re-emission of radiation from atoms which have absorbed light is termed atomic fluorescence. In
1962, Alkemade was the first to suggest that AFS had analytical potential, which was demonstrated in
1964 by Winefordner.
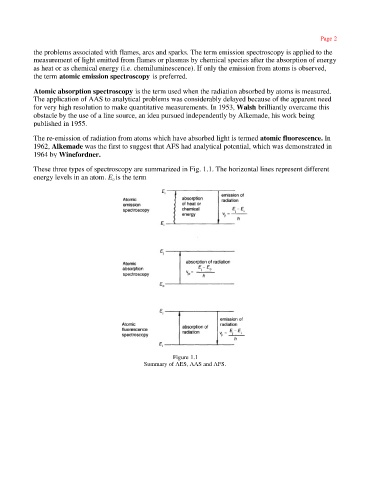
These three types of spectroscopy are summarized in Fig. 1.1. The horizontal lines represent different
energy levels in an atom. E is the term
0
Figure 1.1
Summary of AES, AAS and AFS.