Page 210 - Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
P. 210
Deformation in the context of energy geostructures 183
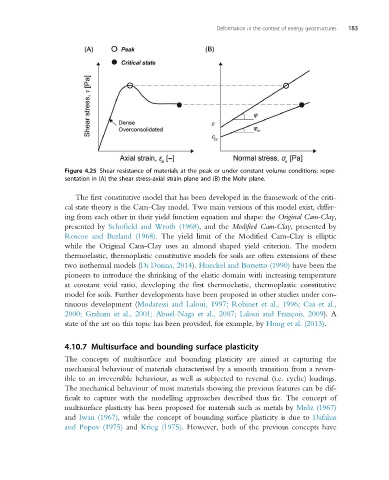
Figure 4.25 Shear resistance of materials at the peak or under constant volume conditions: repre-
sentation in (A) the shear stress-axial strain plane and (B) the Mohr plane.
The first constitutive model that has been developed in the framework of the criti-
cal state theory is the Cam-Clay model. Two main versions of this model exist, differ-
ing from each other in their yield function equation and shape: the Original Cam-Clay,
presented by Schofield and Wroth (1968), and the Modified Cam-Clay, presented by
Roscoe and Burland (1968). The yield limit of the Modified Cam-Clay is elliptic
while the Original Cam-Clay uses an almond shaped yield criterion. The modern
thermoelastic, thermoplastic constitutive models for soils are often extensions of these
two isothermal models (Di Donna, 2014). Hueckel and Borsetto (1990) have been the
pioneers to introduce the shrinking of the elastic domain with increasing temperature
at constant void ratio, developing the first thermoelastic, thermoplastic constitutive
model for soils. Further developments have been proposed in other studies under con-
tinuous development (Modaressi and Laloui, 1997; Robinet et al., 1996; Cui et al.,
2000; Graham et al., 2001; Abuel-Naga et al., 2007; Laloui and François, 2009). A
state of the art on this topic has been provided, for example, by Hong et al. (2013).
4.10.7 Multisurface and bounding surface plasticity
The concepts of multisurface and bounding plasticity are aimed at capturing the
mechanical behaviour of materials characterised by a smooth transition from a revers-
ible to an irreversible behaviour, as well as subjected to reversal (i.e. cyclic) loadings.
The mechanical behaviour of most materials showing the previous features can be dif-
ficult to capture with the modelling approaches described thus far. The concept of
multisurface plasticity has been proposed for materials such as metals by Mrˇ oz (1967)
and Iwan (1967), while the concept of bounding surface plasticity is due to Dafalias
and Popov (1975) and Krieg (1975). However, both of the previous concepts have