Page 28 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 28
Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
6
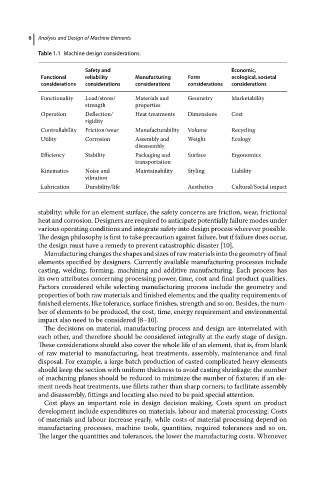
Table 1.1 Machine design considerations.
Safety and Economic,
Functional reliability Manufacturing Form ecological, societal
considerations considerations considerations considerations considerations
Functionality Load/stress/ Materials and Geometry Marketability
strength properties
Operation Deflection/ Heat treatments Dimensions Cost
rigidity
Controllability Friction/wear Manufacturability Volume Recycling
Utility Corrosion Assembly and Weight Ecology
disassembly
Efficiency Stability Packaging and Surface Ergonomics
transportation
Kinematics Noise and Maintainability Styling Liability
vibration
Lubrication Durability/life Aesthetics Cultural/Social impact
stability; while for an element surface, the safety concerns are friction, wear, frictional
heat and corrosion. Designers are required to anticipate potentially failure modes under
various operating conditions and integrate safety into design process wherever possible.
The design philosophy is first to take precaution against failure, but if failure does occur,
the design must have a remedy to prevent catastrophic disaster [10].
Manufacturing changes the shapes and sizes of raw materials into the geometry of final
elements specified by designers. Currently available manufacturing processes include
casting, welding, forming, machining and additive manufacturing. Each process has
its own attributes concerning processing power, time, cost and final product qualities.
Factors considered while selecting manufacturing process include the geometry and
properties of both raw materials and finished elements; and the quality requirements of
finished elements, like tolerance, surface finishes, strength and so on. Besides, the num-
ber of elements to be produced, the cost, time, energy requirement and environmental
impact also need to be considered [8–10].
The decisions on material, manufacturing process and design are interrelated with
each other, and therefore should be considered integrally at the early stage of design.
These considerations should also cover the whole life of an element, that is, from blank
of raw material to manufacturing, heat treatments, assembly, maintenance and final
disposal. For example, a large batch production of casted complicated heavy elements
should keep the section with uniform thickness to avoid casting shrinkage; the number
of machining planes should be reduced to minimize the number of fixtures; if an ele-
ment needs heat treatments, use fillets rather than sharp corners; to facilitate assembly
and disassembly, fittings and locating also need to be paid special attention.
Cost plays an important role in design decision making. Costs spent on product
development include expenditures on materials, labour and material processing. Costs
of materials and labour increase yearly, while costs of material processing depend on
manufacturing processes, machine tools, quantities, required tolerances and so on.
The larger the quantities and tolerances, the lower the manufacturing costs. Whenever