Page 311 - Analysis, Synthesis and Design of Chemical Processes, Third Edition
P. 311
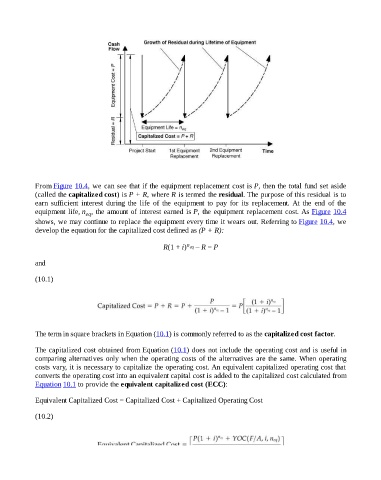
From Figure 10.4, we can see that if the equipment replacement cost is P, then the total fund set aside
(called the capitalized cost) is P + R, where R is termed the residual. The purpose of this residual is to
earn sufficient interest during the life of the equipment to pay for its replacement. At the end of the
equipment life, n , the amount of interest earned is P, the equipment replacement cost. As Figure 10.4
eq
shows, we may continue to replace the equipment every time it wears out. Referring to Figure 10.4, we
develop the equation for the capitalized cost defined as (P + R):
n
R(1 + i) – R = P
eq
and
(10.1)
The term in square brackets in Equation (10.1) is commonly referred to as the capitalized cost factor.
The capitalized cost obtained from Equation (10.1) does not include the operating cost and is useful in
comparing alternatives only when the operating costs of the alternatives are the same. When operating
costs vary, it is necessary to capitalize the operating cost. An equivalent capitalized operating cost that
converts the operating cost into an equivalent capital cost is added to the capitalized cost calculated from
Equation 10.1 to provide the equivalent capitalized cost (ECC):
Equivalent Capitalized Cost = Capitalized Cost + Capitalized Operating Cost
(10.2)