Page 113 - Analytical Electrochemistry 2d Ed - Jospeh Wang
P. 113
98 CONTROLLED-POTENTIAL TECHNIQUES
Example 3-4 A sample containing cadmium gives a polarographic reduction
current of 6.0 mA. The current increases to 9 and 12 mA upon increasing the
cadmium concentration in two steps of 2 mM each. Calculate the cadmium
concentration in the original sample.
Solution
6 KC 9 K
C 2 12 K
C 4
to yield a C value of 4 mM.
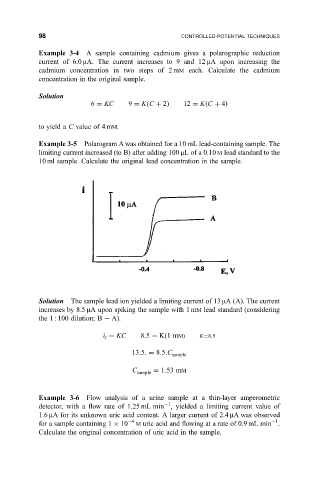
Example 3-5 Polarogram A was obtained for a 10 mL lead-containing sample. The
limiting current increased (to B) after adding 100 mL of a 0.10 M lead standard to the
10 ml sample. Calculate the original lead concentration in the sample.
Solution The sample lead ion yielded a limiting current of 13 mA (A). The current
increases by 8.5 mA upon spiking the sample with 1 mM lead standard (considering
the 1 : 100 dilution; B 7A).
i KC 8:5 K
1mM K8:5
l
13:5: 8:5:C sample
C sample 1:53 mM
Example 3-6 Flow analysis of a urine sample at a thin-layer amperometric
1
detector, with a ¯ow rate of 1.25 mL min , yielded a limiting current value of
1.6 mA for its unknown uric acid content. A larger current of 2.4 mA was observed
1
for a sample containing 1 10 4 M uric acid and ¯owing at a rate of 0.9 mL min .
Calculate the original concentration of uric acid in the sample.