Page 217 - Analytical Electrochemistry 2d Ed - Jospeh Wang
P. 217
202 ELECTROCHEMICAL SENSORS
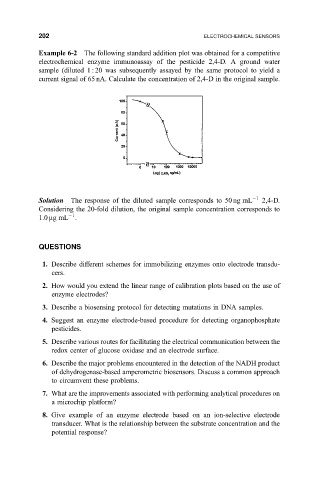
Example 6-2 The following standard addition plot was obtained for a competitive
electrochemical enzyme immunoassay of the pesticide 2,4-D. A ground water
sample (diluted 1 : 20 was subsequently assayed by the same protocol to yield a
current signal of 65 nA. Calculate the concentration of 2,4-D in the original sample.
Solution The response of the diluted sample corresponds to 50 ng mL 1 2,4-D.
Considering the 20-fold dilution, the original sample concentration corresponds to
1
1.0 mgmL .
QUESTIONS
1. Describe different schemes for immobilizing enzymes onto electrode transdu-
cers.
2. How would you extend the linear range of calibration plots based on the use of
enzyme electrodes?
3. Describe a biosensing protocol for detecting mutations in DNA samples.
4. Suggest an enzyme electrode-based procedure for detecting organophosphate
pesticides.
5. Describe various routes for facilitating the electrical communication between the
redox center of glucose oxidase and an electrode surface.
6. Describe the major problems encountered in the detection of the NADH product
of dehydrogenase-based amperometric biosensors. Discuss a common approach
to circumvent these problems.
7. What are the improvements associated with performing analytical procedures on
a microchip platform?
8. Give example of an enzyme electrode based on an ion-selective electrode
transducer. What is the relationship between the substrate concentration and the
potential response?