Page 84 - Analytical method for food addtives
P. 84
22
23
19
21
indicator and the zones, which quench fluorescence,
chromatographed on preadsorbent silica gel of C18
mM sodium
nm; one includes distillation step
2-step extraction and the other used a simple water
extraction. Two methods employ measurement in
Two of the spectrophotometric methods based on
potassium sorbate in sliced cheese was measured
mM berate
and the other includes a 2-step extraction. Fifth
bonded silica gel plates containing fluorescent
measurements in visible region; one utilised a
by penetration time and distance from surface
To determine diffusivity the concentration of
are compared by scanning densitometry
mM sodium cholate, 15
Aliquots of samples and standards are
Additives were separated using a 20
nm
method was a GC–MS method
spectrophotometrically at 300
UV region at 235
buffer with 35
Potassium sorbate concentration in cheese was
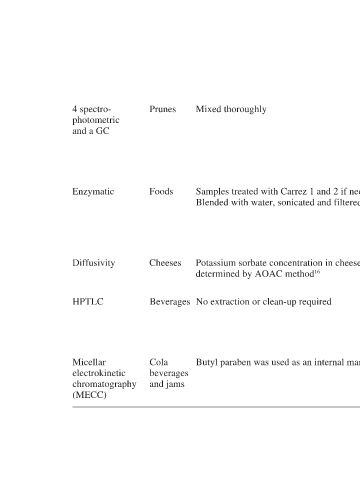
Butyl paraben was used as an internal marker
Blended with water, sonicated and filtered 20 Sorbic acid converted to sorbyl coenzyme A with Samples treated with Carrez 1 and 2 if necessary. acyl CoA synthetase in the presence of coenzyme A and adenosine-5′-triphosphate. Pyrophosphate is hydrolysed with inorganic pyrophosphate to give inorganic phosphate. So
No extraction or clean-up required
determined by AOAC method 16
Mixed thoroughly
Prunes Foods Cheeses Beverages Cola beverages and jams
4 spectro- photometric and a GC Enzymatic Diffusivity HPTLC Micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MECC)