Page 123 - Antennas for Base Stations in Wireless Communications
P. 123
96 Chapter Three
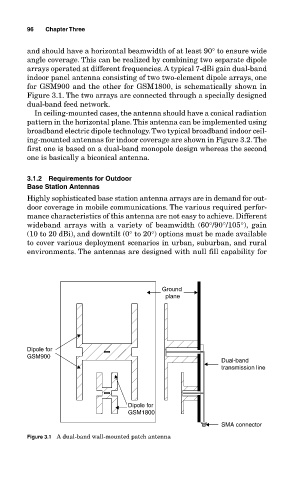
and should have a horizontal beamwidth of at least 90° to ensure wide
angle coverage. This can be realized by combining two separate dipole
arrays operated at different frequencies. A typical 7-dBi gain dual-band
indoor panel antenna consisting of two two-element dipole arrays, one
for GSM900 and the other for GSM1800, is schematically shown in
Figure 3.1. The two arrays are connected through a specially designed
dual-band feed network.
In ceiling-mounted cases, the antenna should have a conical radiation
pattern in the horizontal plane. This antenna can be implemented using
broadband electric dipole technology. Two typical broadband indoor ceil-
ing-mounted antennas for indoor coverage are shown in Figure 3.2. The
first one is based on a dual-band monopole design whereas the second
one is basically a biconical antenna.
3.1.2 Requirements for Outdoor
Base Station Antennas
Highly sophisticated base station antenna arrays are in demand for out-
door coverage in mobile communications. The various required perfor-
mance characteristics of this antenna are not easy to achieve. Different
wideband arrays with a variety of beamwidth (60°/90°/105°), gain
(10 to 20 dBi), and downtilt (0° to 20°) options must be made available
to cover various deployment scenarios in urban, suburban, and rural
environments. The antennas are designed with null fill capability for
Ground
plane
Dipole for
GSM900
Dual-band
transmission line
Dipole for
GSM1800
SMA connector
Figure 3.1 A dual-band wall-mounted patch antenna