Page 502 - Applied Numerical Methods Using MATLAB
P. 502
APPENDIX I
MATLAB
First of all, the following should be noted:
1. The index of an array in MATLAB starts from 1, not 0.
2. A dot(.) must be put before an operator to make a termwise (element-by-
element) operation.
Some of useful MATLAB commands are listed in Table I.1.
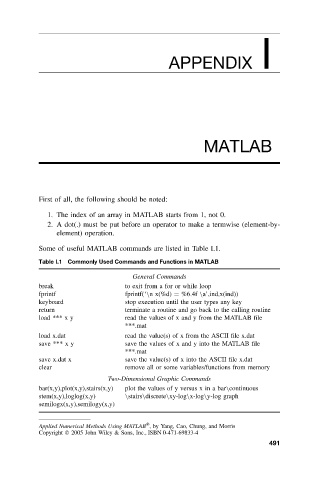
Table I.1 Commonly Used Commands and Functions in MATLAB
General Commands
break to exit from a for or while loop
fprintf fprintf(‘\nx(%d) = %6.4f \a’,ind,x(ind))
keyboard stop execution until the user types any key
return terminate a routine and go back to the calling routine
load *** x y read the values of x and y from the MATLAB file
***.mat
load x.dat read the value(s) of x from the ASCII file x.dat
save *** x y save the values of x and y into the MATLAB file
***.mat
save x.dat x save the value(s) of x into the ASCII file x.dat
clear remove all or some variables/functions from memory
Two-Dimensional Graphic Commands
bar(x,y),plot(x,y),stairs(x,y) plot the values of y versus x in a bar\continuous
stem(x,y),loglog(x,y) \stairs\discrete\xy-log\x-log\y-log graph
semilogx(x,y),semilogy(x,y)
Applied Numerical Methods Using MATLAB , by Yang, Cao, Chung, and Morris
Copyright 2005 John Wiley & Sons, Inc., ISBN 0-471-69833-4
491