Page 210 - Applied Petroleum Geomechanics
P. 210
In situ stress estimate 205
Very high tectonic stresses are found in the Longmen Shan fault belt
near China’s Sichuan basin, where the margin zone between the Tibetan
Plateau and Sichuan basin is located. In this fault belt the rate of the
maximum tectonic compressive strain (ε H ) measured from the surface by
GPS reaches to 40e50 nano-strains per year (Pan and Shen, 2017). This has
imposed large tectonic strains to the Sichuan basin, which can reach
9
ε H ¼ 2e20 10 /yr. If the subsurface formations have the same strain
rates and the rock properties are E ¼ 30 GPa, n ¼ 0.25, and ε h ¼ 0, then
the minimum tectonic stress can be obtained from Eq. (6.28), i.e.,
min 5 4
s tect ¼ 1.6 10 e1.6 10 MPa/yr and the maximum tectonic stress
max 5 4
s tect ¼ 6.4 10 e6.4 10 MPa/yr (refer to Eq. 6.73). The high
tectonic strain rates and high tectonic stresses have caused very high
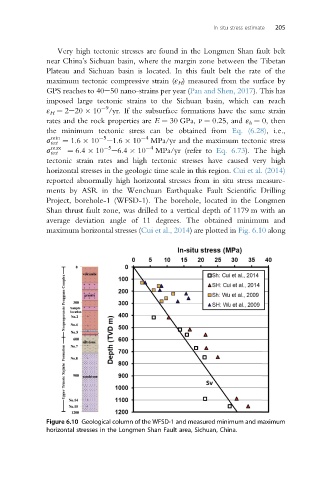
horizontal stresses in the geologic time scale in this region. Cui et al. (2014)
reported abnormally high horizontal stresses from in situ stress measure-
ments by ASR in the Wenchuan Earthquake Fault Scientific Drilling
Project, borehole-1 (WFSD-1). The borehole, located in the Longmen
Shan thrust fault zone, was drilled to a vertical depth of 1179 m with an
average deviation angle of 11 degrees. The obtained minimum and
maximum horizontal stresses (Cui et al., 2014) are plotted in Fig. 6.10 along
Figure 6.10 Geological column of the WFSD-1 and measured minimum and maximum
horizontal stresses in the Longmen Shan Fault area, Sichuan, China.