Page 41 - Applied Petroleum Geomechanics
P. 41
32 Applied Petroleum Geomechanics
Table 2.2 Bulk densities and porosities in various rock types.
3
Rock type Density r b (g/cm ) Porosity f (%)
Granite 2.5e2.8 0.5e1.5
Dolerite 3.0e3.1 0.1e0.5
Limestone 2.5e2.8 5e20
Dolomite 2.5e2.87 1e5
Quartzite 2.65 0.1e0.5
Sandstone 2.0e2.6 5e25
Shale 2.0e2.7 10e30
CoaleAnthracite 1.3e1.6
CoaleBituminous 1.1e1.4
Sediments 1.7e2.3
Metamorphic rocks 2.6e3.0
3
Bulk density (g/cm )
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
0
100
TVD ( m bml) 200
300
400
500
600
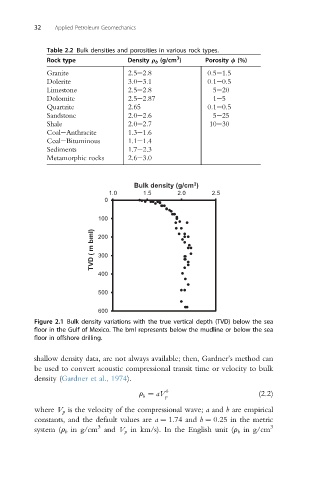
Figure 2.1 Bulk density variations with the true vertical depth (TVD) below the sea
floor in the Gulf of Mexico. The bml represents below the mudline or below the sea
floor in offshore drilling.
shallow density data, are not always available; then, Gardner’s method can
be used to convert acoustic compressional transit time or velocity to bulk
density (Gardner et al., 1974).
r ¼ aV p b (2.2)
b
where V p is the velocity of the compressional wave; a and b are empirical
constants, and the default values are a ¼ 1.74 and b ¼ 0.25 in the metric
3 3
system (r b in g/cm and V p in km/s). In the English unit (r b in g/cm